What rich snippets are and why they can help the SEO
For some people the term may appear vague, even if it is a feature that we have before our eyes every time we use Google Search: we discover something more about rich snippets, one of the additional forms of result that Google shows users, to better understand how they work, how they are obtained and how they can help both the SEO and page visibility.
The evolution of Google SERPs
Up until about 2009, and so just over 12 years ago, search engines presented their results without particular ornaments, and Google itself focused its SERPs simply on the famous, classic and perhaps missed 10 blue links, easy to optimize with a few very raw techniques compared to those of today.
Then came a brand new user interface, which began to use information retrieved through structured page data to provide better, more accurate and enriched results to users, and the evolution has continued to this day, with search results that look very different than the origins, especially on mobile. Depending on the query and the search intent, we can then see extra information under the links, various large blocks of rich content – often visual or action-oriented – and then more side panels, carousels of images or news and so on.
This means, first of all, that it is no longer enough to try to optimize the site to rank among the 10 blue links, as we once did, both because users have evolved, learning to use a different look to quickly scan the results, defined pinball pattern, both because the features take away space and visibility to organic links, as we have shown with our research.
It then becomes very important to know these multimedia results and understand how to intercept them with our content, to take advantage of the visibility opportunities they provide.
What rich snippets are
Over the years, then, Google has evolved to respond to different types of search results and displays designed to better meet the needs of users, and rich snippets are a concrete example of this trend.
Rich Snippets are normal Google search results that show additional data to the user, usually extracted from structured data found in the HTML of a page; such advanced results add visual interest, more information and greater utility to users.
Common types of Rich Snippet include reviews/ratings with the star system, cooking times and calories on recipe results, schedules and locations in event listings, product prices and the name of the author who edited that content.
Google uses rich snippets to improve the results it shows and provide key information directly in its SERP page; according to experts, the results with Rich Snippet are more appealing than normal search results, and this can lead to a higher organic CTR: in particular, some studies show that users click on multimedia results 58 percent of the time, compared to a 41 percent CTR for non-rich results.
The definitions of snippets, rich results and SERP features
We did not randomly use the expression rich results: for many analysts, in fact, rich snippets are essentially rich results or multimedia results of Google Serps, although it is actually possible to make a more precise distinction – whereas, however, that Google documentation does not use consistent or precise terminology.
Many, then, interchangeably use the term multimedia result or rich results with rich snippet, and this can create confusion with respect to the distinctive features of these two elements, without forgetting the presence of SERP features and featured snippets that further complicate things. Here then is a possible terminology, with the definitions of the main terms:
- Snippet: the snippets are the classic information shown among Google results (and other search engines) for any query. The snippet is composed by the title (title tag), the meta description and the url of the ranking site.
- Rich Snippet. It is, as the name indicates, a fragment enriched with additional elements shown to the Google user. They are therefore normal search results that however have some extra data, usually positioned between the URL and the description.
- Rich results or multimedia results are various types of search results enhanced by visual information, taken from relevant structured data. Here is a list of the types of rich results that appear in Google Search
- SERP features are all those features that appear on the Google search results page in addition to the standard blue link list: knowledge graph, PPC ads, local pack, carousels of images and featured snippets are just some types of SERP features.
Some types of multimedia results – such as Product, Podcast, App software (currently in beta version) and Sitelink – add additional information and/or functionalities to an existing search snippet (result); other types of multimedia results add a completely new functionality to the SERP, such as in the case of recipe or movie carousels, job listings boxes, How To carousels and more.
In this perspective, therefore, rich snippets can be considered a type of multimedia result, while other features, such as Faqs, are a type of multimedia result but also a SERP feature.
Rich snippets and SEO: why they are important and how they help our site
Now that we have a clearer idea of what rich snippets are, we can also analyze the benefits they provide in terms of SEO.
We should not, however, think of a direct influence on ranking since, as clarified several times by Google, the use of structured data on the page does not represent a ranking factor: this information serves only to communicate to Google more precisely the content factors of the page, such as the entities that are the object of the content.
As previously mentioned, however, there is a concrete effect on the CTR: the rich snippets have a higher click rate than the other results, because simply people prefer to click on the results that provide them already starting more information, who convince them of the choice. In addition, the stars of the reviews, the miniature images and other items shown by Google add more space to the page in the SERP, which can thus attract more user attention.
Simplifying, if the percentage of clicks of a snippet increases, the page gets more organic traffic from that search result, resulting not from an improved location in the search engine, but just from an increase in clicks by people.
In the long term, however, this trend could also affect the ranking itself: the more people click on the result thanks to the rich snippet, the more Google will notice that people prefer that page over other competitors. This is a potential indirect signal of authoritativeness, which may indicate to Google that that page is a good result for that specific search, which can lead to improvements in rankings over the long term.
The typologies of rich snippets
The types of rich snippets are many, but in many cases apply only to a very specific type of site, such as flight information, books or movies.
These are some of the most common types of Rich Snippet, activated with the specific markup.
- Product
It is an essential element for e-commerce sites, which through structured data can transmit to search engines information about a specific product, such as price, images, availability and reviews, which will be visible by users in its rich snippet in SERP.
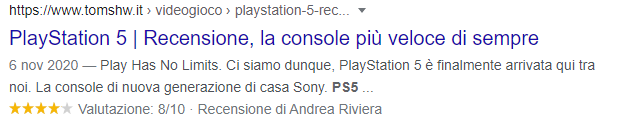
- Review
The reviews markup makes the star ratings appear under a snippet in the search results: the score scale goes from 1 star, lower value, to 5 stars, maximum value. This rich snippet can report information from a single reviewer/reviewer or aggregate user reviews, and star ratings are also displayed in the relevant knowledge panel.
- Recipes
This special type of structured data only applies to recipes and shows some specific features, such as cooking time or dish preparation, ingredients, images, calories and user ratings.
- Organization
It helps Google understand and show key information about an organization (such as a company), including address, logo and contact information.
- Events
This markup reports important details, such as the date, time, location and other event.
- Video
Search engines may not be able to “watch” videos on the page, but with this structured data we can facilitate their understanding of the video content.
- Article
Adding this marking to the news page, blog or sports articles may enable some additional features, such as making it a part of Google Top News.
- Music
This rich snippet allows you to view additional information about the artist in question such as the record label and the musical genre, or even the release dates of the albums.
- Film
The films snippet shows the details of the director, the release date, the duration and the box office proceeds, in addition to the star rating based on reviews.
How to optimize the page for rich snippets
To activate a rich snippet is therefore an incredible opportunity for the SEO, and in order to succeed in this objective we must therefore proceed in two ways: to understand which type it makes sense for our contents and for our field of activity and, consequently, optimize the page by adding the right and specific markup of structured data, which then will be tested and finally released effectively.
The work on structured data
The optimization for rich snippet includes several best practices, starting with the use of structured data of Schema.org.
The structured data, in fact, allow us to optimize the content for the snippet including all the basic information it needs, depending on the type of data already present in the vocabulary of Schema.org, a real complete dictionary of the types of data, default by topic and sector.
Google supports the structured data of Schema.org, which are mapped to individual entities based on what Google already has in its database: “using the structured data of Schema.org, optimize for these entities”, summarizes Brian Harnish. In addition, all major search engines support this language, so we do not have to worry about adapting Schema.org to other search engines other than Google.
A simple search on the Schema.org site is enough to find the right match of the type of data for the entities and topics we are working for, and once we have identified, we just have to encode the markup.
In a nutshell, we can use standard HTML structured data or JSON-LD structured data, and the Google developer documentation contains additional information that is useful in identifying the steps to be taken according to our needs.
The next step is to test the data we added to the page with the new Google test for multimedia results, the tool that replaced the deprecated structured data test tool. The test process is generally quite simple, because it is enough to copy the code from our page, insert it in the appropriate field of the tool and then launch the test, which highlights any errors present: for more information, we can refer to Google’s advice to optimize rich results.