Segnali sociali: cosa sono oggi e quanto servono alla SEO?
È da almeno dieci anni che si discute di social signals per la SEO, e per la precisione si cerca di determinare se i cosiddetti segnali sociali (generalmente intesi come numero di follower e di interazioni sulle varie piattaforme) abbiano una correlazione diretta al ranking del sito e se, quindi, sono un fattore che può influenzare la visibilità di un sito web nei risultati di ricerca. Nonostante le smentite e i chiarimenti di Google, questa teoria continua ancora a fare capolino, ed effettivamente potrebbe avere un fondo di verità: per dirla più semplicemente, l’autorevolezza conquistata sui social potrebbe effettivamente dare una spinta positiva al sito su Google, a patto di non considerare i SEO social signals come fattore di ranking diretto, ma come uno dei tanti elementi “esterni” che contribuiscono a rafforzare il brand online.
Cosa sono i social signals
I social signals o segnali sociali sono una metrica integrativa sull’interazione delle persone con i contenuti pubblicati su social network e piattaforme come Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, Reddit, Medium e così via; questi segnali includono tutte le azioni che definiscono il coinvolgimento degli utenti, come recensioni, commenti, Mi piace, Non mi piace, condivisioni, voti, pin, visualizzazioni, link e così via, e sono usati per comprendere il livello di popolarità e affinità per un contenuto specifico.
I segnali social sono quindi tutte quelle attività che avvengono sui social media e che possono essere associate a un sito web o a un brand, indicatori tangibili dell’interazione degli utenti con i contenuti che si manifestano all’interno delle piattaforme social sotto forma di azioni dirette che gli utenti compiono in risposta a ciò che trovano interessante o rilevante.
Più precisamente, quindi, tali social signals sono la metrica usata per individuare l’interazione umana e l’engagement dei post sui social media, e tra i più noti ci sono:
- Mi piace, commenti e condivisioni su Facebook.
- Mi piace, retweet, citazioni e conversazioni su X (ex Twitter).
- Pin, visualizzazioni e commenti di Pinterest.
- Connessioni, link e riferimenti di LinkedIn.
- Follower, commenti e regram su Instagram.
- Visualizzazioni, pollici in su (o in giù) e commenti su YouTube.
Più alto è il numero di Mi piace, condivisioni, visualizzazioni e clic che un post ha sui social, più è visibile e più in alto si posiziona nel feed dello specifico social media.
I segnali sociali e Google, un tema controverso
Nel tempo, i segnali social e di engagement sono diventati una metrica chiave del social media marketing, perché rivelano quali sono le tipologie di contenuto che maggiormente interessano il target e quali modalità di comunicazione fanno maggiormente presa.
Inoltre, aumentare mi piace, condivisioni e visualizzazioni significa anche rendere più visibili i post, e quindi aumentare le possibilità di aumentare la platea di persone che leggono, apprezzano, condividono e fanno clic sui post: semplificando, alcuni post sui social media possono portare a milioni di condivisioni, mi piace, visualizzazioni e clic, spesso anche verso il sito.
Per questo motivo, già dal 2010 si è iniziato a speculare su un possibile legame diretto tra social signals e SEO, arrivando a inserire questi segnali tra i 200 fattori di ranking di Google; in realtà, fonti dello stesso motore di ricerca hanno smentito questa correlazione, ma ciò non ha fatto crollare il mito.
A rinfocolare i fautori di questa teoria sono anche le parole di Matt Cutts, che proprio nel 2010 aveva definito le “pagine social come segnali di ranking”, che svolgono un ruolo nella SEO organica – nell’ottica del ragionamento che “più follower hai e più traffico devii al tuo sito dai social media… migliore è il tuo ranking di ricerca”. Tuttavia, quelle affermazioni risalgono agli albori della SEO moderna (ad esempio, il Panda Update arriva solo nel 2011, per non dire degli interventi successivi), e lo stesso Cutts le corresse nel 2014, dicendo che Google non usa i dati dei profili dei social media come segnali di ranking (questo articolo ricostruisce tutta la storia con le fonti originali).
Sia John Mueller che Gary Illyes, successivamente, hanno confermato che i segnali sociali non hanno un impatto diretto sul ranking di Google e che, specificamente, non sono presi in considerazione da RankBrain, e il motivo sta nella scarsa affidabilità dei social signal come metrica: i follower possono essere acquistati, mi piace e commenti possono essere falsati e sono solo metriche di vanità e così via.
SEO social signals e ranking
Possiamo quindi affermare con sicurezza che i social signals di un sito e di un brand non influenzano direttamente e causalmente il suo ranking su Google, ma comunque c’è qualcosa in più da dire – motivo per cui è importante lavorare bene sui social.
Non possiamo infatti trascurare che c’è comunque una correlazione latente e indiretta con le classifiche, perché i segnali social rafforzano per certi versi la SEO del brand e del sito per una serie di motivi.
Ad esempio, sono fattori di ranking tra l’altro i backlink, la capacità di intercettare l’intento di ricerca, la qualità dei contenuti, la freschezza (per alcune query) e l’autorevolezza: attraverso i post sui social network, l’engagement generato e la visibilità ottenuta (sintetizzati dall’espressione SEO social signals) possiamo segnalare a Google che stiamo pubblicando e condividendo contenuti che soddisfano il search intent, sono pertinenti e autorevoli, di alta qualità e freschi, e magari conquistiamo anche backlink ai contenuti grazie al passaparola social, perché contenuti apprezzati, interessanti e curati diventano più facilmente condivisibili.
C’è poi un altro aspetto da non trascurare: se Google ufficialmente non usa i segnali sociali per il suo ranking, sembra che altri motori di ricerca alternativi come Bing prendano invece in considerazione tali parametri per le loro classifiche, e Mi piace, le condivisioni, le visualizzazioni e i clic sui social possono influenzare le classifiche di ricerca di tali search engine.
In linea generale, l’obiettivo dei motori di ricerca è classificare e promuovere contenuti che interessino e coinvolgano i lettori: le metriche comportamentali degli utenti, che includono i segnali sociali, possono rappresentare un modo per determinare la pertinenza di una pagina rispetto a una query di ricerca, alla luce dell’equazione che più un contenuto viene visualizzato, condiviso, apprezzato, commentato, maggiori sono la sua qualità, valore e rilevanza.
A cosa servono i segnali social
Questa è la tesi portata avanti (ancora oggi) da chi sostiene il valore SEO dei social signals, ma questa causalità è come detto smentita dalle parole dei Googler e anche dagli studi specifici.
In senso più ampio, è difficile (per non dire impossibile) certificare se, quanto e come i social possano avere un impatto sul posizionamento di un sito e influire sulla visibilità di brand nei motori di ricerca, ma possiamo comunque provare a elencare alcuni dei possibili effetti positivi di un buon lavoro sui social.
- Migliorare il traffico e le prestazioni dei contenuti del sito
Il primo modo di sfruttare i social è usarli come cassa di risonanza per condividere ogni contenuto del piano editoriale della nostra azienda, brand e sito – che altrimenti rischia di essere disponibile solo per gli utenti (limitati) del sito.
Molto semplicemente, i social ci permettono di avere accesso a un pubblico molto più ampio di quello che avremmo solo sul sito, portando quindi a un incremento del traffico (sia da una ricerca organica che attraverso le reti stesse); a sua volta, ciò può portare al miglioramento di altri segnali di qualità di questi contenuti, come engagement, visibilità e durata, che potrebbero determinare un impatto indiretto anche sul ranking. Un utilizzo strategico di questo canale parte da un’apposita analisi competitor social, che consente di verificare le mosse dei principali avversari per inidviduare le strategie che stanno dando frutti migliori.
- Più opportunità di ottenere backlink naturali
La condivisione via social non porta solo più traffico ai nostri contenuti, ma aumenta anche le possibilità che ottengano backlink: spesso basta una sola condivisione per far aumentare esponenzialmente la visibilità di un post e, avendo più lettori, ci sono maggiori opportunità di ricevere link naturali ai contenuti che hanno conquistato l’interesse del pubblico.
- Posizionamento di brand
I profili social possono svolgere un ruolo importante per monopolizzare le keyword branded, posizionandosi insieme alle pagine classiche del sito.
Rispetto a queste ultime, le pagine social possono offrire agli utenti una visione diversa della nostra attività, fornendo informazioni aggiuntive per coloro che lo desiderano, al punto di poter rappresentare una possibile spinta verso la definitiva conversione (o, al contrario, scoraggiando l’azione).
- Creazione di fiducia
La SEO serve (anche) a creare fiducia nel pubblico target: i consumatori oggi hanno a disposizione un numero enorme di opzioni, e quindi sono alcuni “dettagli” che fanno la differenza e portano alla scelta finale.
In tal senso, i profili sui social media possono servire a corroborare le opinioni su un brand e ad accrescere il senso di fiducia verso quel marchio, mentre social media scadenti o inesistenti possono essere un campanello d’allarme per gli utenti. Inoltre, i social offrono la possibilità di umanizzare il marchio, andando oltre alla semplice presentazione dei prodotti/servizi e caratterizzandosi in maniera più distinguibile rispetto ai competitor.
- Rafforzare la brand awareness
I social media sono forse il luogo in cui oggi si fa branding, e una buona presenza sulle varie piattaforme può aiutare gli sforzi nella brand awareness, che sappiamo avere un effetto positivo indiretto anche sulla SEO: sintetizzando all’estremo, i profili social possono aiutare ad attirare potenziali clienti che, a loro volta, conoscono il marchio e ci entrano in contatto, fino alla possibile conversione.
In tal senso, serve anche un lavoro di controllo della web reputation, ricordando che la stragrande maggioranza delle persone ottiene informazioni dalle recensioni online e che una quota crescente di utenti basa le proprie decisioni di acquisto sui post di Facebook o sulle recensioni di YouTube.
- Aumentare le ricerche locali
Anche la SEO locale può avvantaggiarsi di una presenza positiva sui social network, perché spesso le SERP legate a query commerciali presentano elenchi di attività ricavate da piattaforme come Facebook, Yelp e ovviamente Google My Business (oltre a Tripadvisor per il settore food, ad esempio, estendendo il concetto).
Come detto prima, i feedback e le recensioni sono cruciali anche per il marketing SEO locale, tanto che secondo alcune statistiche rappresentano il 13% dei fattori di ranking per le ricerche locali e il 7% per le ricerche generali.
Social signals, una prospettiva diversa sul loro significato
Oltre alla classica definizione di social signals, c’è un altro modo di interpretare questa espressione e di legarla al modo in cui gli algoritmi di Google comprendono le relazioni tra le entità, che è quello che il nostro Ivano Di Biasi scriveva già nel suo libro sulla link building.
In questo senso, i segnali social non sono la semplice conta delle interazioni su piattaforme social, ma sono le informazioni provenienti da pagine web che Google usa per organizzare dati e relazioni del suo “social graph“, il grafo che studia e analizza le entità e il modo in cui sono legate tra loro in base alla popolarità presso le persone. Nel suo costante sforzo di comprendere meglio i contenuti e la loro rilevanza per gli utenti, Google utilizza queste entità e le loro relazioni per costruire una comprensione più profonda del web: i segnali social, in questa nuova accezione, includono la frequenza con cui un’entità viene menzionata nei contesti social, la reputazione e l’autorità delle fonti che fanno queste menzioni, e la coerenza e la contestualizzazione di queste menzioni all’interno di discussioni più ampie.
Tra gli elementi valutati dall’algoritmo ci sono valutazioni del tipo “quante persone parlano del brand”, “quanti linkano al tuo brand”, “a chi viene associato il tuo brand” e “quanto è famoso chi cita il brand”, e ogni azione nel social graph è un segnale sociale.
Queste informazioni sono vitali per far capire a Google chi è il brand, quanto vale, in quale contesto esiste, cosa ne pensano le persone online, da chi è riconosciuto come autorevole, e in concreto possono essere menzioni e citazioni al brand o all’URL del sito – che possono servire anche al calcolo della Share of Voice, come sappiamo.
Conoscere i segnali sociali è importante nella strategia di ottimizzazione off page e nella costruzione di un profilo backlink naturale: se nessuno conosce il nostro brand e nessuno ne parla online, è difficile giustificare tonnellate di backlink frutto solo di campagne di link building condotte in maniera aggressiva, e Google ci può mettere poco a verificare l’inconsistenza di questa autorevolezza, esponendo il sito al rischio di una penalizzazione.
Le statistiche sui social network in Italia
In conclusione, i social media sono diventati parte integrante della vita online e hanno completamente cambiato il modo in cui comunichiamo e prendiamo decisioni, e pertanto è inevitabile pensare che ci possano essere dei segnali social SEO. Ufficialmente, per Google non è così e questi segnali non hanno peso per il ranking direttamente, ma in qualche modo possono influenzare indirettamente le considerazioni degli algoritmi circa la qualità e l’interesse dei contenuti pubblicati.
I numeri descrivono meglio le potenzialità di questo bacino: secondo Audiweb, noi italiani trascorriamo online da mobile 2 ore e 36 minuti nel giorno medio, con punte di oltre 3 ore per i 18-34enni,
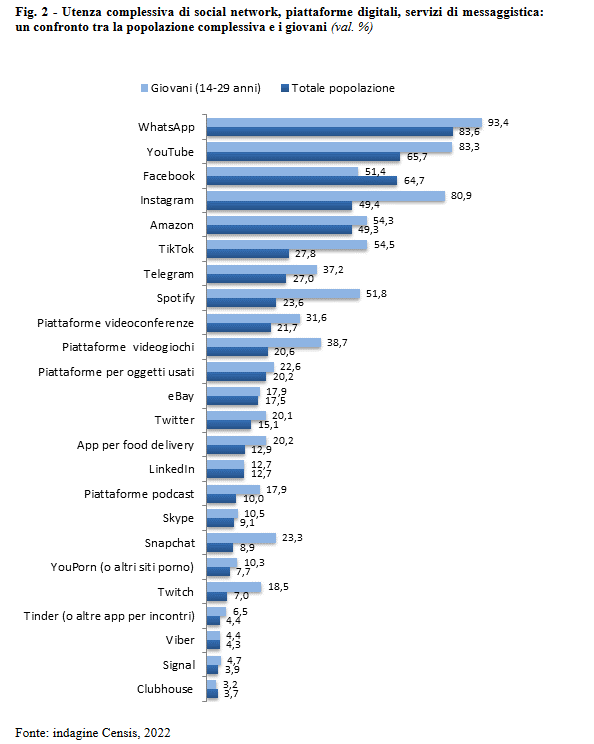
Ancora, il 18° Rapporto sulla comunicazione del Censis certifica che l’82,2% degli utenti visita e utilizza proprio social network, distribuendosi tra le tante piattaforme come di seguito mostrato.
E se le cifre relative alla fascia d’età tra i 14 e i 29 anni sorprendono relativamente poco (il 92,4% utilizza WhatsApp, l’83,3% YouTube, l’80,9% Instagram, il 64,7% Facebook, il 54,3% Amazon, il 31,6% le piattaforme per le videoconferenze, il 51,8% Spotify, il 54,5% TikTok, il 37,1% Telegram, il 20,1% il fu Twitter), anche tra i più anziani (65 anni e oltre) i social network si fanno largo, visto che gli utenti dal 42,0% al 51,4%) e gli utenti aumentano dal 36,5% al 47,7% in un solo anno.
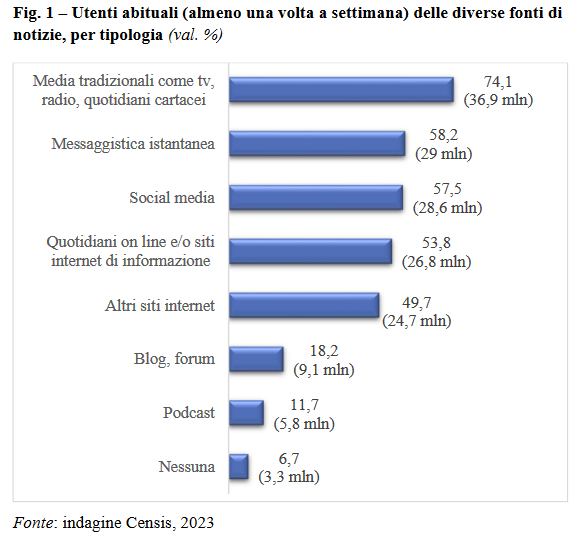
I social si stanno imponendo non solo come mezzo per mantenere un contatto “virtuale”, ma anche e sempre più come fonte di informazione, come dimostra quest’altro report del Censis, che analizza in maniera più ampia il tema della disinformazione e delle fake news, certificando che più della metà della popolazione attiva online, pari a 28,6 milioni di persone, si serve appunto delle piattaforme social in maniera abituale per trovare e leggere notizie di attualità.
Italiani e social media
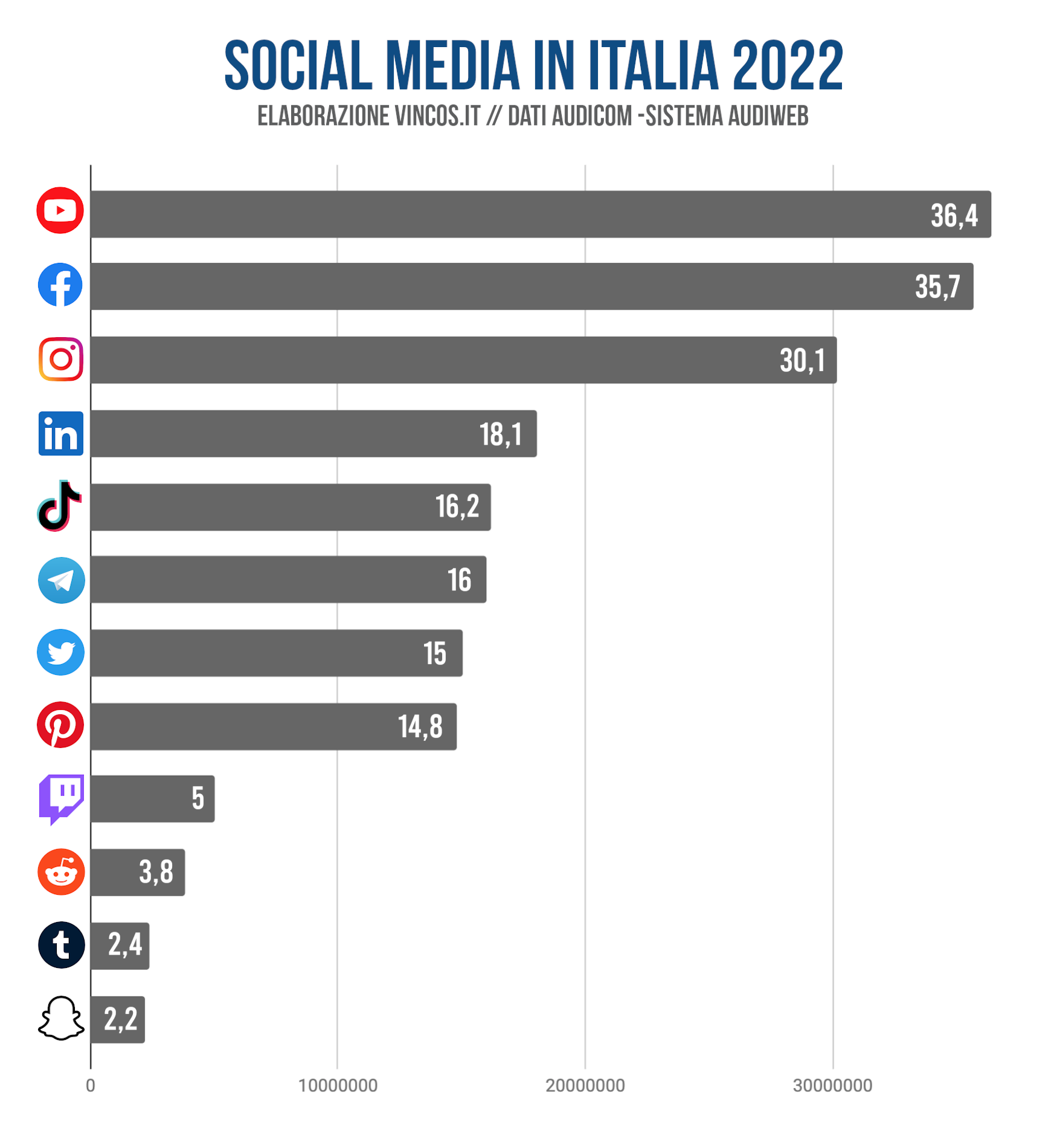
Vanno ancora più nel dettaglio i dati di Vincos, basati sul consuntivo 2022 dei social media in Italia: lo scorso anno gli italiani hanno dimostrato una predilezione per YouTube, che ha dominato la scena dei social media con un’affluenza media mensile di 36,4 milioni di utenti, segnando un incremento del 3% e superando di poco Facebook, che invece ha attirato circa 35,6 milioni di persone al mese, con un aumento del 2%. Instagram ha completato il trio di testa, registrando 3.,1 milioni di utenti, in crescita del 6%.
Qui iniziano le grandi novità ed evoluzioni: LinkedIn ha conquistato la quarta posizione, detenuta nel 2021 da Pinterest, e ha raccolto un seguito di 18 milioni di persone. TikTok, con un impressionante salto del 68%, ha raggiunto 16,2 milioni di utenti e, osservando i dati dei primi mesi del 2023, l’app di origine cinese ha continuato a espandere la sua base di utenti, avvicinandosi ai 21 milioni a maggio, secondo le ultime statistiche sui social media.
Telegram si è piazzato al quinto posto con 16 milioni di utenti, nonostante un decremento del 6%, ed X (Twitter, acquisita da Elon Musk verso la fine del 2022), ha visto una crescita del 31%, raggiungendo poco più di 15 milioni di utenti, con i numeri di maggio che indicano un ulteriore aumento fino a 18 milioni.
Pinterest segue con 14,8 milioni di utenti, ma ha subito una flessione del 28,5%. Le piattaforme di nicchia chiudono la classifica: Twitch, nonostante una riduzione del 47,5%, conta su 5 milioni di utenti; Reddit cresce del 28% arrivando a 3,8 milioni; Tumblr aumenta del 33% con 2,4 milioni; e Snapchat sale del 17% con 2,2 milioni di utenti.
Nonostante non sia stato il social con il maggior numero di visite, Facebook ha comunque mantenuto il primato per il tempo speso dagli italiani sulla piattaforma, con una media mensile di 13 ore per utente nel 2022, in aumento rispetto alle 11 ore e 29 minuti del 2021. Instagram si è collocato al secondo posto con 6 ore e 39 minuti di utilizzo medio, seguito da YouTube con 5 ore e 13 minuti. TikTok ha registrato un tempo medio di utilizzo di 4 ore e 49 minuti, segnando un’ora in più rispetto all’anno precedente.