Google Search, best practices for the SEO of ecommerce sites
eCommerce sites are the new front of Google’s commitment to updating support and support documents: in fact, in the pages of the Google Search Central guides, a set of guide pages on best practices for eCommerce in Google Search has been published, explaining how to create the best eCommerce site possible for users and search engine.
SEO for eCommerce, Google’s best practices
This is not the first time that Google offers advice to e-commerce, but now those who work in the sector have a series of super detailed documents, which should be controlled by every SEO and any eCommerce activity that has ambitions of organic visibility.
In the introduction, we read that “being discovered is a fundamental challenge for any eCommerce site”, and that “the acquisition of customers and the creation of a relationship with them is an important factor of business growth“; in this sense, it is not enough just to know how to create an eCommerce, but it is necessary to acquire the right online visibility, so that Google can help buyers discover the site at every stage of the purchase process.
This set of guides is designed for developers who are building websites and want to make sure that the site works well with Google. The focus is on online trading sites, but many of the points are equally relevant to sites that list products available only in physical stores.
When we share eCommerce data and site structure with Google, it still says the introductory document, “Google can find and analyze your content more easily, which allows your content to be viewed in Google Search and other Google platforms” and this “can help buyers find your site and your products”.
Google’s 7 guides to SEO for eCommerce
At the moment, the Google Help Docs dedicated to eCommerce – which follows the updating of the documentation on search operators and the guide to HTTP status codes, network problems and DNS errors, for example – is divided into seven more detailed pages, each of which is dedicated to a specific focus.
To be precise, this is the list of indications and best practices recommended by Google, with reporting of the main information contained:
- Where eCommerce content can be viewed on Google, which describes the different Google platforms in which the contents of eCommerce sites can appear.
- Sharing product data with Google, which analyzes the methods to be used to share product data with Google.
- Including structured data relevant to the eCommerce, which invites you to provide “explicit information about the meaning of your page with structured data“, to help Google understand and present your content appropriately.
- How to launch a new eCommerce site, which contains tips to strategically launch a new eCommerce website and understand the considerations on timing when registering your website with Google.
- Designing a URL structure for eCommerce sites, with best practices to avoid problems related to scanning and designing specific URLs for eCommerce sites.
- Helping Google to understand the structure of the eCommerce site, to be able to design a site navigation structure and link pages to help Google understand what is most important on the site.
- Page layout, incremental page loading and their impact on Google Search, dedicated to common UX templates for eCommerce sites and find out how they affect Google’s ability to scan and index content.
Main tips for eCommerce sites
We can quickly deepen the information contained in this extensive documentation, which help us to outline the framework of actions needed to launch an eCommerce site and increase its visibility in Google Search.
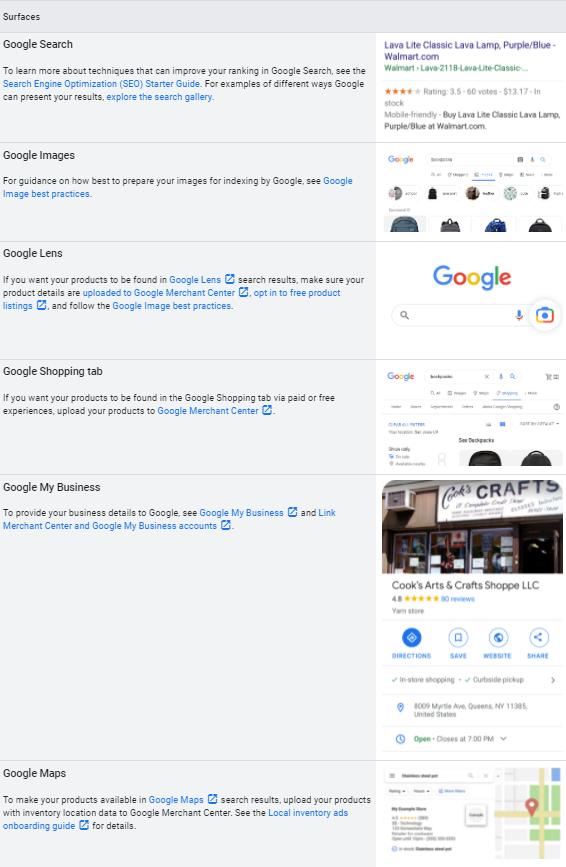
Google offers several platforms where content can be viewed in the e-commerce field, and, in addition to Google Search, the most common platforms are Google Images, Google Lens, the Google Shopping tab, Google My Business and Google Maps. Each has its own specific characteristics and purposes, but some tips can be useful to optimize the content in order to meet the different needs of customers.
In particular, Google invites you to edit both product data and catalog (using informative descriptions of products that match the search terms used by customers), but also to describe the company history and promotional offers during special seasonal sales, to provide in-depth reviews of the products we sell and to accept feedback, ratings and reviews from customers to help new buyers better understand the products offered. Other good practices include the creation of training or education to the use of products (for example workshops or lessons that can increase engagement with customers), the creation of direct interactive streaming (to show products, clarify their use and answer questions in real time) and improve customer service touchpoints.
Indications of technical SEO for eCommerce sites
Google Helps documents also focus on technical SEO interventions for eCommerce sites and, in particular, on the best ways to correctly communicate the data of the products of our site, including appropriate structured data that can improve the accuracy of Google’s understanding of the content.
Among the markups that can be adapted to a commercial site, also because they can activate specific rich results among SERPs that users will find at different stages of their purchase path, are mentioned, for instance, LocalBusiness (for location and opening times, among other things), Product, Review, BreadcrumbList, WebSite, VideoObject, HowTo and FaqPage.
Still on the technical side, then, Google reminds us the importance of using a well-designed URL structure, because so crawlers can locate and retrieve more efficiently the web pages on the site, but also avoid indexing problems that are frequent. Specifically, the guide recommends limiting the URL parameters and managing them from a SEO perspective, and then again to minimize the number of alternative URLs that return the same content, to verify that each page in the page layout has a unique URL and to use talking URLs (which can help Google to better understand the page), among other things.
Very important is also to take care of the navigation structures of the site (such as menus and links between pages), which may affect Google’s understanding of the structure of the site: the basic objective is to set up a crawler friendly system, that allows Google to find and reach through links all pages of the site, but it is also useful to promote the best categories or products of eCommerce. As a general rule, Google documentation reminds us that “the more links you receive a page within a site, the greater the relative importance of the page compared to the other pages of the same site”, and so we can use internal linking (with links from the home page, newsletter or blog posts) to highlight the page of a product particularly sold.
Google guides to the SEO of eCommerce sites
The last two aspects covered by Google’s extensive support documentation for eCommerce sites concern elements of UX and some strategies to launch a new site online.
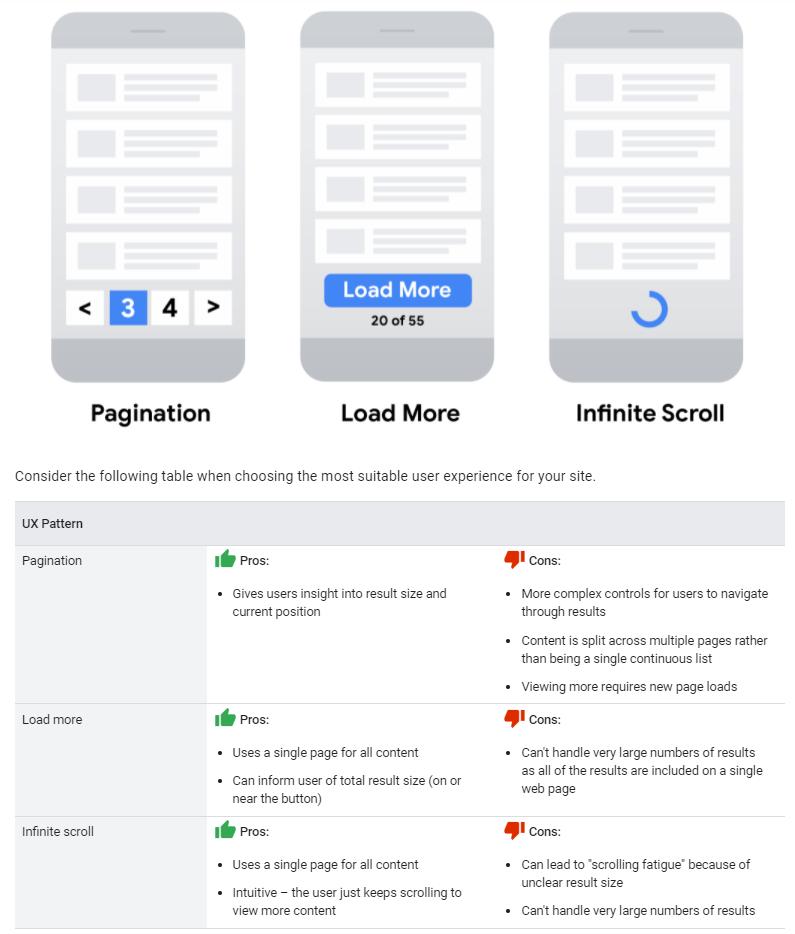
Today more than ever the user experience is crucial, having become part of the ranking factors used by Google with the Page Experience Update: to improve this aspect, we can show a subset of results not to overload the page performance, checking that the Google crawler can find all the contents of the site.
There are three tools in this sense – pagination, load more and infinite scroll – and we can choose the one that best suits our site and user behavior.
This way, for example, we can upload partial results for user search results, category pages, blog posts or newsletter titles in the archive, user reviews, comments to blog posts. This incremental content loading, in response to user actions, can benefit the UX because the loading of the home page is faster than loading all the results at once; it reduces network traffic, particularly important for mobile devices; improves backend performance, limiting the volume of content recovered from databases or the like; improves reliability, avoiding excessively long lists that could reach the limits of resources leading to errors in the browser and backend systems.
Finally, the page dedicated to those who are about to launch a new eCommerce emphasizes not only the importance of performing some technical steps to register the domain on Google (such as registering at Google Merchant Center and checking the property in Search Console) but also the role that some immediate marketing strategies may have.
There are four, in particular, approaches that can be experienced when starting a commercial project, each with its pros and cons:
- Grand reveal: makes the entire site live to the public and to Google at the same time.
- Homepage launch: initially makes available to the public and Google only the home page of the site.
- Launch without product availability: launches the complete website to the public and Google, but the products are marked as “sold out”.
- Soft Launch: enables all aspects of the site as soon as they are ready for production, but provides a separate marketing event for the “official” launch.