Black hat SEO: 17 techniques to know and avoid in a strategy
Looking for shortcuts and faster solutions to reach a goal, even in an unscrupulous way, is perhaps a natural feature of the human being, and the SEO field is no exception. In addition to regular and official practices, which respect the limits set by the Google Webmaster Guidelines, many techniques have been developed with blurred outlines or openly in violation of the rules, which – as we know – are defined Black hat SEO. Google has become very good at identifying and penalizing such black hat techniques, but this does not prevent people from trying them, despite exposing themselves to the risk of an algorithmic or manual penalty.
Playing against Google’s rules
The Black Hat SEO takes its name from the old cowboy movies in which the bad guys wear a black hat and actually who performs such techniques is likely to end – sometimes even unknowingly – in the list of bad guys according to Google.
To continue to be the most popular search engine in the world and provide users with the most useful results, Google must continually update its algorithm and try to limit the presence of irrelevant results or openly spam ones. The rules of the game – so to speak – are set by webmaster guidelines and are open to everyone, from web developers to SEO professionals.
Nevertheless, there are many people who want to win the game by circumventing the rules and then bring in illegal techniques: the professionals of Black Hat SEO know the rules of search engine optimization, but they use this understanding to take shortcuts that are not exactly provided for in Google’s best practices.
This mode is in contrast to the white hat SEO professionals, who to win in the SERP instead follow the guidelines for webmasters of Google, promote high value content, engage in in-depth keyword researches and so on.
17 Black hat SEO techniques to know and avoid
It is important to mention that these forbidden tactics are not always carried out voluntarily, so it is good to familiarize yourself with the SEO black hat to be sure to proceed only with lawful strategies. Then, let’s take a look at 17 famous and widespread black hat practices to avoid because they can result in an algorithmic or manual Google penalty, following the suggestions of Jon Clark on Search Engine Land.
Illegal techniques on links
Because of their weight and value, links are probably the first element on which the attention of those who intend to force Google rankings, leading to the adoption of a series of prohibited behaviors.
- Link purchase
A relevant and high-quality link can drive traffic to a domain and at the same time tell the Google algorithm that it is a reliable source.
A good backlink can also help Google map a site, allowing the crawler to have a better idea of the project’s central topic, making it easier to decide when and how to show pages in search results.
The purchase of a link, however, is against the Instructions for Google webmasters and, according to Google, it does not work; moreover, those who are caught may suffer a penalty or manual action that affects specific pages or, worse, the entire site.
Google keeps track of links that “are likely to have been purchased and those that have been earned” and is able to identify unnatural patterns behind backlinks, even for the Google’s properties themselves.
- Exchange of products for links
Whether the site is offering or taking, the exchange of free products (or discounts) for links is considered by Google a link scheme, a link scheme.
To avoid this problem, just mark the link with a rel = “nofollow” tag, to signal search engines not to follow the link for ranking purposes.
- Link inside the footer
The footer has often been used as a favorite place for inserting a link, because it is displayed on every page of a site. Google is however able to identify (and penalize) the use of links in footers with commercial anchor text on a large scale to manipulate the results.
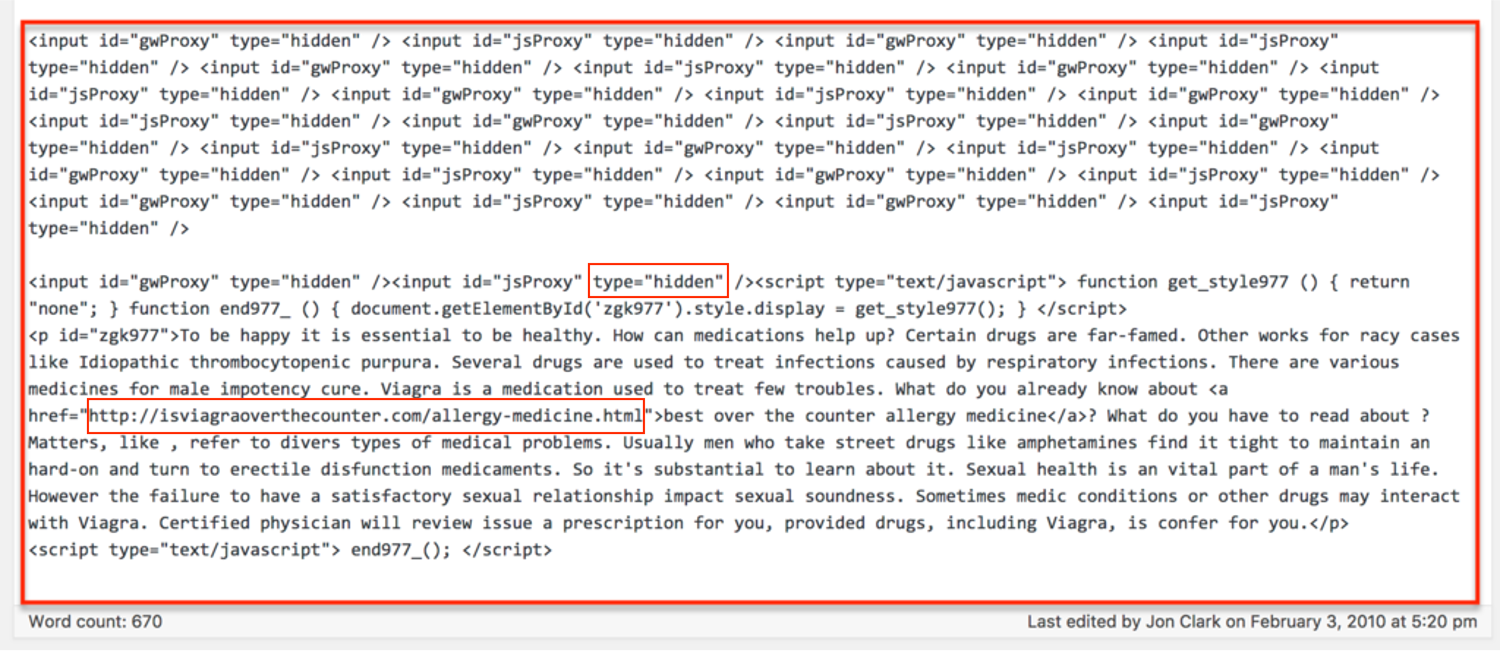
- Hidden links
It is kind of a bit old technique, but sometimes you still happen to find: to hide a link in the text of the site or show the link in the same color as the background. Needless to say that Google may notice these gimmicks and will penalize those who tried to play with the system; in addition, including a high number of irrelevant links also means diluting the relevance and offering to Google “Fewer reasons to drive traffic to your target audience”.
Deceptively hidden links are a violation of Google guidelines, and that means:
- Do not hide text behind an image.
- Do not keep the text off the screen using CSS.
- Do not use a font size of 0.
- Do not make a link a small string of characters, like a period.
- Spam in comments
Another technique used in the past is to insert a link to a site in the comments section of another domain: today automatic systems often block the attempt, but in any case it is better to “avoid doing so unless the link is not relevant”, useful and in topic – and anyway should not generate effects in terms of link building. Otherwise, you risk a penalty for spam.
- Abuse of anchor text
Apparently it makes sense to “match the title of your page every time you share a link to it, because the title is the subject of your page and consistency could imply relevance”, but from Google’s point of view this is likely to prove to be a lazy spamming.
On the contrary, the anchor text should be short, relevant to the linked page, not full of keywords and unique, as well as placed in the context of the surrounding environment, of which it is a natural part.
This rule applies to both internal and external links.
- Malicious backlinks
Google’s attention to links can also be used for malicious purposes: “some black hat SEO professionals can exploit in their interest the Google penalty system to drag down your page rank by inserting links in websites you don’t want to be associated with,” says Clark.
It is for this reason that, for ten years now, Google has created the system of link disavow, which allows you to deny backlinks received from any unwanted domains and to dissociate your site from the suspicious or harmful one.
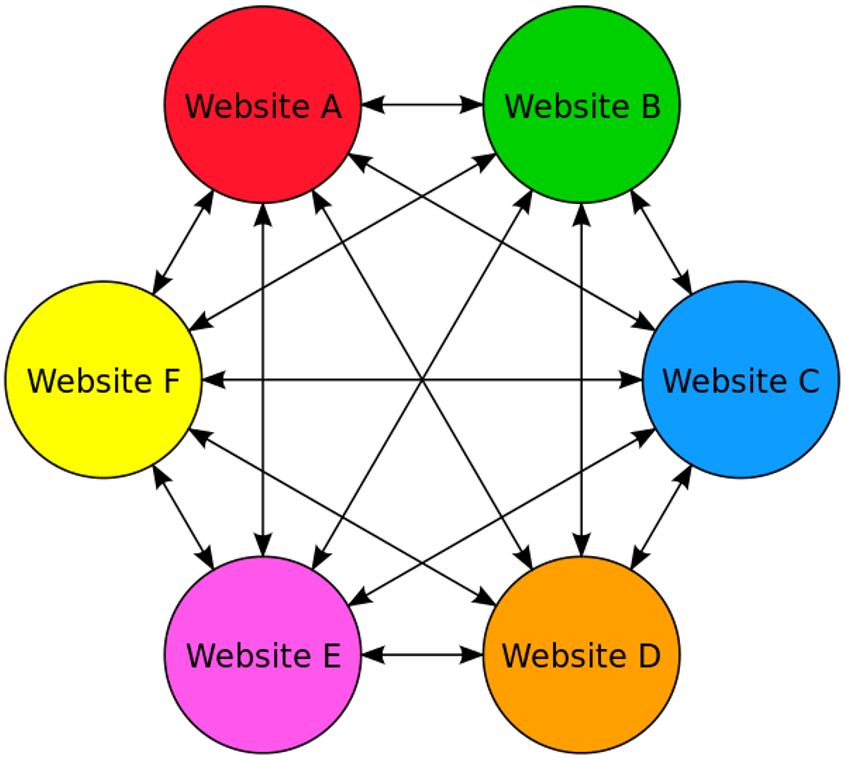
- Use of PBNs
PBNs – or Private Blog Networks – are essentially linked websites; very popular in the 1990s and early 2000s (“particularly among the fan pages of different television programs, films, musicians, etc.”), they are not necessarily a bad thing, but these chains are considered a link scheme when used to manipulate algorithms and rankings.
Black hat techniques on content
Some black hat tactics focus on content instead and try to take advantage of some folds of the Google rating system to speed up the climb to the first page.
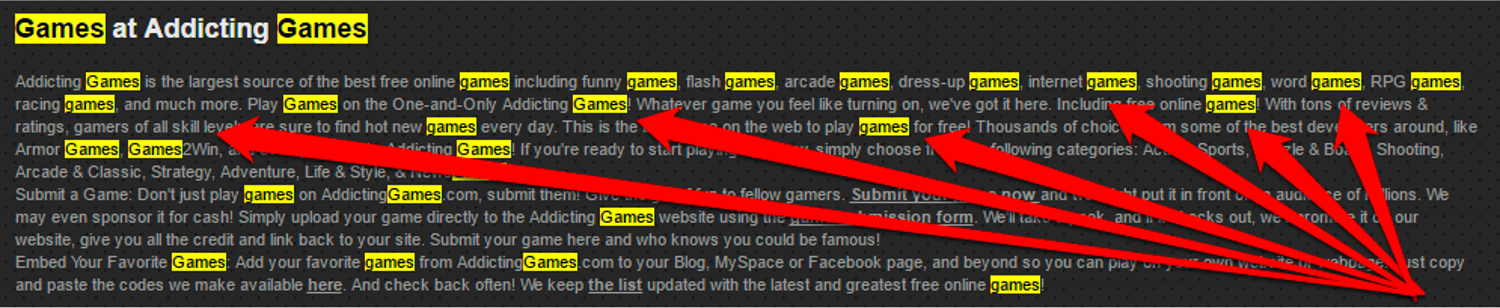
- Keyword stuffing
It is (unfortunately!) a bad habit that continues to be present: to stuff the text with repetitions of the keyword for which you try to position the page, creating the effect of keyword stuffing that is annoying even when reading.
Moreover, it starts from two wrong assumptions, namely that you have to build a page/text around a keyword (while you have to center the search intent) and that you just have to repeat the keyword in block to rank first.
In fact, Google rewards those who provide high-quality information and “semantically-linked keyword-rich content”, rather than those that “simply bear superficial marks”.
- Keyword stuffing inside the alt-text of images
Even the misuse of keyword in the alt tags of an image can damage the positioning of the site, in addition to representing improper use of this element and to provide substantially a disservice to visitors.
- Hidden content
As with hidden links, hidden content too has the same background color in order to “include as many key phrases as possible, long-tailed keywords and semantically linked words on a page”.
Obviously, the Google algorithm can detect the difference between keywords within the body of a paragraph and hidden keywords in the background.
In addition to being inserted intentionally by the site owner, hidden content may also depend on other situations:
- Posting a guest post that includes hidden content.
- Comment system not be strict enough and therefore not able to detect hidden content.
- Website hacked by hackers who post hidden content (parasite hosting).
- Accidental insertion of an authorized user, who copies and pastes text with the CSS style from a different source.
Not all hidden content is prohibited – the rule of thumb is that “content is fine as long as the content is visible to both the user and the search engine” – and for example can be deemed lawful “content visible only to mobile visitors, but hidden to desktop visitors”.
- Plagiarized or duplicate content
Duplicate content – both as the result of scraping or real plagiarism – may violate copyright or brand laws; moreover, since “Google wants to share high quality domains, plagiarism is a reason for sanction”.
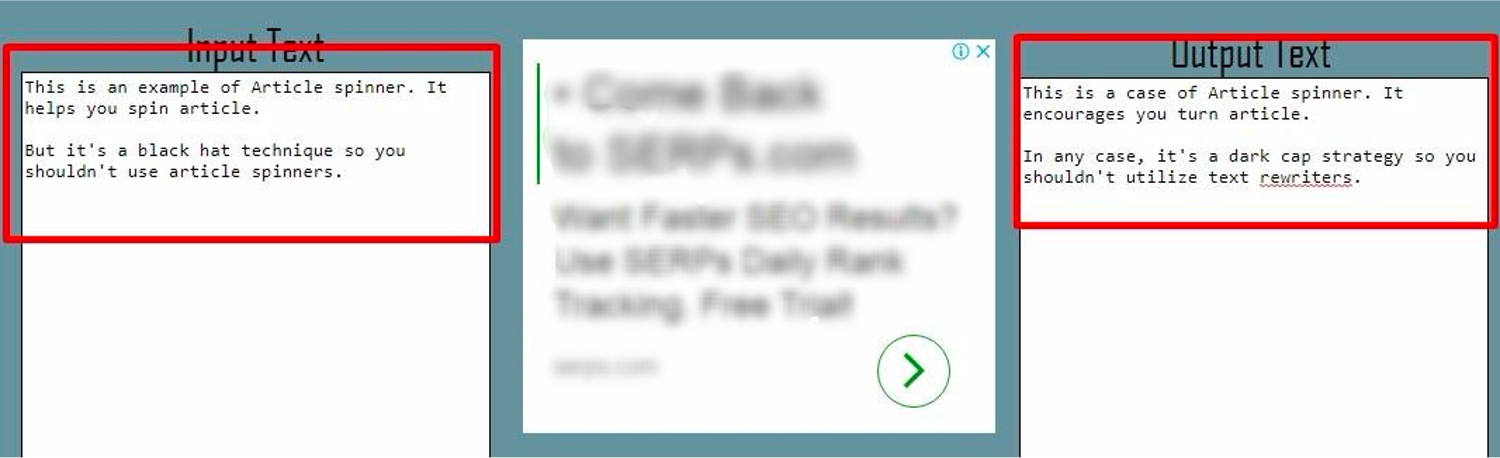
- Article spinning
Article spinning is a technique that involves rewriting content using synonyms, changing the structure of the sentence or rewriting the text entirely but without changing the information of the source material.
Article spinning can be done manually or using technology, and as advanced as it can be, Google will continue to penalize sites that use this technique, because such articles “degrade the quality of the Internet”.
- Rich Snippet Spam
Rich snippets are snippets with additional information, which therefore can drive more traffic, but there are many ways in which the scheme used to generate these fragments can be manipulated.
- Cloaking
Cloaking is an old black hat trick that is still used today: it employs a flash or animated page to hide information from visitors, which only Google can see in HTML.
If Google senses this tactic it will punish the site with a penalty.
- Doorway pages
Doorway pages are a form of concealment, designed to classify themselves for certain keywords but then redirect visitors to other pages.
They are also known by other names, such as Bridge pages, Portal pages, Jump pages, Gateway pages, Entry pages.
- Compromised website
Having an unprotected site is not a penalizing factor per se, but can cause harm in the event of hacker attacks and violations, leading to the loss of the ranking.
If the site undergoes an attack or an injection of malicious code and Google discovers it, can block the domain for people using the search engine: this “not only will it make you lose the trust of anyone who visits the site from organic research, but it will cause the website to fall into the rankings”, just as if it had been hit by a penalty.
Black hat SEO, techniques that are destined to have a short life
The rewards of the black hat route are generally short-lived and “are also immoral since they worsen the Internet”.
However, it is important to be aware that, in addition to white hat and licit tactics, there are also black hat tactics that are wrong and dangerous, from which it would be better to stay away.
Without forgetting that, in case of accidental penalties or decision to change bad practices, there are ways to recover from Google’s penalties and raise the rankings of a site.