Podcasts: what they are, what they are for, and how they are created
It is accessible and extremely usable content, capable of intercepting an audience that is not always interested in other media and of gathering positive opinions. Although between lights and shadows, particularly related to monetization possibilities, the podcast is confirmed as an effective format for communication. And indeed, the number of podcasting products and podcasters continues to increase, even in Italy, also a sign of a profound transformation in the way we consume media products. In this article we delve into this world, trying to answer essential questions such as what is a podcast and why is it called that, but above all to explore the origins, evolution and revolutionary impact that this product has had in the world of digital marketing. We will also take a step-by-step look at how to create your own podcast, what equipment is needed, and why this format can become a key pillar in modern SEO strategies.
What is a podcast
A podcast is recorded digital audio content that is distributed via the Internet and can be enjoyed on-demand on various devices such as smartphones, tablets and computers. Usually organized into series and episodes, podcasts are available for download or streaming through dedicated platforms such as Apple Podcasts, Spotify and YouTube Music.
In fact, this system uses a data transmission infrastructure and specific client programs, called “aggregators” or “feed readers,” that allow users to automatically receive new episodes as soon as they are published.
Simply put, we can imagine it as a tailored radio program: instead of having to adhere to a broadcast schedule, a podcast is listened to when and where we prefer, using any Internet-connected device. This makes podcasts particularly flexible and adaptable to our busy lifestyles.
They also span a wide range of topics, from fiction stories to market analysis, from interviews with experts to educational lectures. But, broadening the horizons, the offerings of the podcast world are nothing short of endless, and there is something for every taste: the most common are broadcasts of a journalistic nature, but you can listen to language courses, cooking podcasts, audio on the economy, technology, and even SEO!
The variety is virtually endless, and the possibility of enjoying this content during our daily commute, while exercising or simply relaxing at home is one of the reasons for their enormous success.
What is podcast: definition and meaning
Although the term is now part of our daily lexicon, its precise definition may not be clear to everyone and actually ties in with various curiosities.
The word podcast is in fact a portmanteau, or neologism derived from the union of two terms: “iPod,” Apple’s famous media player launched in the early 2000s, and “broadcast,” which in English means to transmit. In fact, according to the most widely accepted hypothesis, the verb podcasting, which encompasses the set of technologies and activities required to make a podcast, would have originated first – and more precisely, podcasting is the method of distribution and enjoyment of digital content, typically in audio or video format, made possible thanks to technologies that allow automatic downloading of files through the Internet.
These words were invented by British journalist Ben Hammersley, who in 2004, in his article in The Guardian newspaper, talked about the “Audible Revolution” and wondered what to call this phenomenon, proposing variants such as GuerillaMedia, Audioblogging and precisely Podcasting, on which then fell the choice of the international community – so much so that already in 2005 the term Podcasting was named “word of the year” by the U.S. New Oxford dictionary.
Interestingly, this focus came about around 2004, a time when MP3 players such asApple’s iPod were becoming very popular, leading to the construction of completely digital schedules that were far removed from the classic schemes.
In any case, from the very beginning podcasts and podcasting harkened back to the concept of providing audio content that could be easily downloaded and listened to on the go.
Although today podcasts are available on a wide range of devices and platforms, the name has stuck, becoming a synonym for on-demand digital audio content and going on to define not only content consumed via MP3 players, but any type of audio file distributed over the network.
Currently, the term “podcast” is used in a very versatile way and also includes video podcasts, which combine visual and audio elements.This linguistic evolution reflects the adaptability of the format itself, which continues to grow and expand, embracing new technologies and new ways of enjoying content.
The history of podcasting: how podcasts came about and what they are today
The fascinating history of podcasts thus begins in the early 2000s, a time when the Internet was beginning to rapidly expand into daily lives and mobile devices were gaining popularity. The basic idea was as simple as it was revolutionary: make audio files available that could be downloaded and listened to on a delayed basis, breaking the limits of traditional real-time radio broadcasting.
The two key figures were Dave Winer and Adam Curry: Winer, a well-known software developer, and Curry, a former MTV VJ, combined their skills to create the first software capable of automating the downloading of audio files. This software allowed users to subscribe to specific RSS feeds and automatically receive new episodes of a podcast as soon as they were published, ushering in the era of podcasting.
The simplicity of the concept enabled an incredible democratization of the medium: virtually anyone with a microphone and a computer could become a “podcaster.” This accessibility brought an explosion of creativity and diversification, with podcasts covering an endless array of topics, genres and styles. From investigative journalism to history lessons, from interviews with prominent personalities to fiction stories, there was no limit to the topics that could be covered.
As technology has advanced and production costs have dropped, the quality of podcasts has improved significantly, attracting not only independent creators but also large media outlets and corporations. Platforms such as Apple Podcasts, Spotify, and Google (first with Google Podcasts and, after its deprecation, with YouTube Music) have played a crucial role in large-scale dissemination, making podcasts easily accessible to millions of users worldwide. Recently, the format has evolved further with the introduction of video podcasts, which combine visual and audio elements, and integration with artificial intelligence to suggest personalized content to users.
Today, podcasts are not only a cultural phenomenon, but are also a powerful digital marketing and brand-building tool. Companies are using podcasts to tell stories, share experiences and create a direct dialogue with their audience, taking advantage of the intimacy and authenticity that this format can offer, offering new opportunities for both creators and listeners.
The podcast in Italy: origins and evolution
Podcasts landed in Italy somewhat later than in English-speaking countries, but they quickly found fertile ground among listeners and content creators.
Among the first to experiment with this new format was Claudio Sabelli Fioretti with his program “Un giorno da pecora,” which was one of the pioneers in transposing radio content into podcast format. In fact, podcasting was initially used by radio stations simply as a technology to make traditional programs available on demand outside of airtime, but it quickly evolved into its more mature direction.
Another example of a historic podcast is “Scientificast,” which was started in 2007 by a group of researchers passionate about popular science: this project has not only endured over time, but has evolved to become one of the benchmarks for science in Italy, demonstrating the potential of podcasts to cover complex topics in an accessible way.
In the decade that followed, the increasing availability of smartphones and the spread of streaming platforms facilitated access to podcasts, contributing to their popularity. Today, the podcasting scene in Italy is extremely diverse, with numerous independent creators and companies exploiting this channel to promote educational, informational and entertainment content. Some of the most-watched podcasts at the moment include “ Alessandro Barbero‘s podcast,” “Muschio Selvaggio” (originally featuring Fedez and Luis Sal, which was at the center of various issues and legal questions) and “The Essential” by Will Media. These examples show a trend toward the production of high-quality content, often supported by platforms that invest in professional equipment and targeted marketing strategies.
The current landscape also sees the entry of large media outlets and cultural institutions using podcasts to extend their reach and engage younger audiences: museums, universities, and publishing houses are increasingly launching their own podcast channels to offer exclusive content and delve into topics related to their mission.
Podcasting: numbers, statistics and curiosities in the world and in Italy
The podcast phenomenon has experienced explosive growth in recent years both globally and domestically. According to a 2021 report by Edison Research and Triton Digital, more than 116 million Americans, or about 41 percent of the U.S. population over the age of 12, listen to podcasts monthly. In addition, there has been a significant increase in weekly listening hours, with an average of 8 hours of audio content listened to through podcasts per listener.
The numbers in Italy are equally encouraging. Research conducted by Politecnico di Milano’s Digital Innovation Observatories in 2022 found that about 14 million Italians listen to podcasts regularly, or 24 percent of the Italian population aged 16 and older. The growth of podcast listening in Italy has also been fueled by the COVID-19 pandemic, which has led many people to look for new ways to entertain and inform themselves during the lockdown period.
Some interesting facts about podcasts include the fact that mobile devices are the primary means of listening: about 74 percent of listeners use a smartphone to enjoy the content. Also according to the Edison Research report, the favorite genre of American listeners is “comedy,” while in Italy current affairs, information and culture podcasts dominate the scene.
Another significant finding concerns the level of engagement. Podcast listeners tend to be very loyal and immersed in the content. A Spotify study found that about 81 percent of listeners follow at least one podcast each week, and 42 percent of podcast consumers listen to the entire episode without interruption. This level of loyalty is particularly attractive to brands and advertisers, who see podcasts as an opportunity to make deeper connections with audiences.
Contrary to what one might think, then, longer episodes are often very successful: many listeners prefer episodes that last between 30 minutes and an hour, providing enough time for in-depth exploration of the topics covered. This indicates that podcasts are not just consumed as “bite-sized entertainment,” but as content that requires and deserves the commitment of listeners’ time.
Podcasts in Italy: lights and shadows
Podcasts in Italy have thus emerged as a form of entertainment and information that is increasingly appreciated by a diverse audience that is difficult to reach through traditional media. However, this evolution also presents some challenges and critical issues that deserve to be analyzed in order to fully understand its potential and limitations.
According to a recent research conducted by OBE in collaboration with BVA Doxa and published in Il Sole 24 Ore, as many as 13 million Italian listeners have turned to this form of content in 2022, with 53 percent of respondents saying they listen to podcasts on a regular basis. Italian listeners spend an average of 22 minutes a day listening to podcasts, a figure that indicates a growing trend and opens the door to new job opportunities in the sector. In 2023, the number of podcast users was about 11.9 million, representing 39 percent of Internet users between the ages of 16 and 60, up from 36 percent in the previous year. This audience is confirmed to be young, educated and highly professional, profiles that are often difficult to reach with other media.
Interest in podcasts is driven by specific, targeted content. Thirty-two percent of listeners choose to listen to a podcast because of their interest in a specific topic, but other stimuli also emerge, such as suggestions from news sites, social posts, and recommendations from podcast platforms. Interestingly, under-35s are more likely to be guided by influencers in their choice of content than adults. This indicates significant potential for branded content-based marketing strategies, although the quality of the content continues to play a crucial role.
Despite the rise of the format, some shadows remain. Advertising investment in podcasts in Italy is still limited, garnering less than 10 million euros, despite the potential shown at the audience data level. Those involved in buying and selling advertising on podcasts seem not yet to have been able to fully capitalize on the potential offered.
Monetization represents a gray area: with millions of people listening to podcasts every month, the economic potential of this market remains partly unexplored. Another interesting fact is the growing presence of branded podcasts, series sponsored by companies, banks and foundations: in 2023, 61 percent of Italians listened to a branded podcast, a decline from 74 percent in 2022. This decline is attributed to the evolution of the increasingly demanding audience and the increase in the amount of available offerings. However, the impact of branded podcasts on brand perception remains strong, although 41 percent of listeners believe they are too commercial and 51 percent would listen to more if they were more interesting.
Finally, recollection of advertisements associated with podcasts is growing, with 78% of listeners recalling advertising campaigns, particularly those of branded podcasts. This growth also translates into concrete actions such as information search (28%), word of mouth (22%), and purchases (15%).
For the sector to reach its full potential, it will therefore be crucial to continue innovating and investing in high-quality content, exploring new forms of collaboration and sustainable business models.
What podcasts look like: distinguishing characteristics
Going deeper with the analysis of this product, podcasts have distinctive traits that differentiate them from other forms of digital content, and which are also their strengths.
On-demand usability is one of the main features: unlike traditional radio programs, podcasts can be listened to at any time and place, offering great flexibility to users. On-demand delivery also means that each listener can manage content according to his or her own needs, pausing and resuming listening at will, something that was unthinkable with old media such as radio or television.
Accessibility is another strength of podcasts: all it takes to listen to them is a simple Internet-connected device, such as a smartphone, making them easily available to a wide audience.
Another key feature is niche targeting: podcasts can be highly specialized, covering very specific topics that appeal to a niche audience. This level of specialization is difficult to achieve by traditional media. They also foster a high degree of interactivity: listeners can usually interact directly with creators through comments, e-mail and social media, creating a community around the content.
Finally, podcasts also offer format flexibility: since they are not constrained to a specific length, they can range from a few minutes to several hours, providing ample space for in-depth insights and detailed narratives, but most importantly, favoring division into series and related episodes, which creates audience engagement and retention.
What are the different types of podcasts
Podcasts have evolved into a wide range of formats and genres, each with its own style and target audience.This variety makes them not only accessible and interesting to a wide range of listeners, but also gives content creators the flexibility to express their creativity in unique ways.
Among the most popular formats are narrative podcasts, which are true audio narratives: perfect for those who like to immerse themselves in well-constructed stories, whether they are pure fiction or based on real events, narrative podcasts have the ability to transport listeners to new worlds through the magic of storytelling and high-quality audio production, which can capture the imaginations of millions of listeners around the world.
Then there are educational podcasts, a format that focuses on the dissemination of specific information and knowledge. These podcasts cover a wide range of topics, from science to history, technology to philosophy.Often presented by experts in the field, educational podcasts not only disseminate, but also invite reflection and debate. Their intrinsic value lies in their ability to make complex concepts accessible to a wider audience, serving as a valuable resource for anyone wishing to enrich their knowledge in a convenient and enjoyable way.
One of the most popular formats is interview podcasts, in which the central element is the conversation between the host and one or more guests. These podcasts are popular because they offer the opportunity to discover new and different points of view on various topics, thanks to the dynamic and often spontaneous interaction between the interviewees. Interviews can focus on celebrities, industry professionals, or people with unique life stories, creating content that is both informative and engaging.
With the advent of video streaming technologies, the video podcast has gained popularity. This format combines the visual element with the audio element, providing an even richer viewing experience. Video podcasts are particularly effective for tutorials, demonstrations, and content that benefits from visual support: they allow viewers to see facial expressions, body language, and other forms of nonverbal communication that add depth to the narrative or discussion.
In addition to these main categories, there are many other variations that reflect the diversity of human interests and forms of expression. For example, there are commentary podcasts, where presenters analyze current events, and diary podcasts that offer a window into the daily lives of their creators; still, there are business podcasts that explore the world of work and business, providing practical advice and useful insights for professionals, and the aforementioned branded podcasts.
The differences between podcasting and other types of media content
Podcasts have carved out a significant niche because of their unique characteristics. However, to fully understand the distinctive value of podcasts, it is essential to compare them with other forms of media content, so that we can see how podcasting fits into a world where video, radio, and blogs dominate the digital scene, and understand what role it can play in our communication and entertainment strategy.
In general, the main differences lie in the characteristics of accessibility, flexibility of enjoyment, and ability to create an intimate bond with the listener-a unique combination that makes podcasts an increasingly popular choice for those seeking a convenient and engaging way to consume digital content.
Going into more detail, we can think of radio as an example, perhaps the most immediate reference. While radio programs follow a linear schedule and seek to appeal to a broad audience with generalist content, podcasts offer the flexibility of being listened to anytime and anywhere, even offline, once downloaded. This feature makes them particularly suitable for those with busy lives who want to enjoy content during commutes or breaks.
Creative freedom is another point of differentiation: podcasts generally do not have to be subject to the same restrictions imposed by radio stations, in terms of duration, content and format. A podcast episode can last five minutes or two hours, depending on narrative or informational needs, and can be structured in any way the creator sees fit. This flexibility is also reflected in the topics covered, which can be explored in depth without the pressure of having to conform to a predefined schedule grid.
In addition, podcasts are interactive on a level that traditional radio rarely achieves. Listeners can easily leave comments, send emails or interact with creators via social media, creating a direct and immediate line of communication that enriches the listening experience. This type of interactivity not only increases listener engagement, but also provides authors with valuable feedback that can guide future content creation.
Finally, monetization in podcasts has evolved in ways that commercial radio has not yet fully experienced: integrated sponsorship models, dynamic ads, donations through platforms such as Patreon, and access to premium content are just some of the avenues through which podcasters can generate revenue, offering more varied and often more sustainable solutions than traditional radio advertising.
The approach to standard video content is also different: podcasts require fewer production resources and can be consumed without the need for a screen, making them ideal for listening in situations where using video is not practical, such as while driving or exercising. Although there are similar formats such as videocasts, which combine visual elements with audio content, podcasts maintain a simplicity that makes them easier to produce and enjoy, focusing solely on the auditory aspect. The lack of a visual element allows listeners to use their imagination, making the experience more personal and immersive.
Finally, we can think of a comparison with blogging, in terms of sharing and relating: the audio medium offers a more intimate experience, however, and the presenter’s voice can convey emotions and intonations that written text cannot replicate, creating a stronger emotional bond between creator and listener.
Comparison and differences between podcasts and streaming
But there is another distinction to be made, that between podcasts and streaming, which connote as two precisely different modes of enjoying digital content, each with its own peculiarities and advantages. Although both terms refer to the consumption of audio and video files via the Internet, the differences in their approaches, characteristics, and uses are significant.
Podcasting focuses on the distribution of on-demand content that users can download and listen to at any time and place. This flexibility is one of the main strengths of podcasting. Podcasts are organized into episodes and series, often following a narrative or thematic thread that creates a lasting bond between the content creator and the listener. The ability to download episodes for offline listening further enhances convenience, making podcasts ideal for listening during travel, physical activities, or moments of relaxation. In addition, the human voice, a central element in podcasts, builds a more intimate and personal experience than other forms of media. This emotional engagement is difficult to replicate with written text or even video.
Streaming, on the other hand, focuses on transmitting content in real time, requiring a continuous connection to the Internet-meaning that users can start enjoying content almost instantaneously, without having to wait for a full file download. This makes streaming particularly suitable for live events, webinars, sports broadcasts, concerts and live news. Streaming offers a high degree of real-time interactivity, allowing viewers to actively participate through comments and direct questions, which can be immediately answered by content creators. This immediacy and capacity for interaction are distinctive elements that make streaming particularly effective for content that benefits from a participatory dimension.
Unlike podcasts, which can be highly specialized and aimed at specific niche markets, streaming tends to serve a wider range of interests and media needs because of its ability to provide both live and on-demand content. However, the need for a continuous connection somewhat limits the flexibility of consumption compared to podcasts that can be played offline.
Both formats have characteristics that make them unique and complementary. Podcasts, with their flexibility and ability to build an intimate relationship with the listener, offer particular value for those seeking detailed insights and easily accessible content at any time. Streaming, with its immediacy and interactivity, is ideal for events that require instant engagement and active audience participation.
The reasons for the passion for podcasting
Among the reasons for the boom in podcasting, a number of characteristics of this product should be mentioned, starting with the creation of a more direct relationship between the person running the podcast and his or her audience, which convinces, wins over, and builds loyalty, especially among younger audiences. In addition, this medium never disconnects entertainment and in-depth analysis and enables multiple possibilities for interaction.
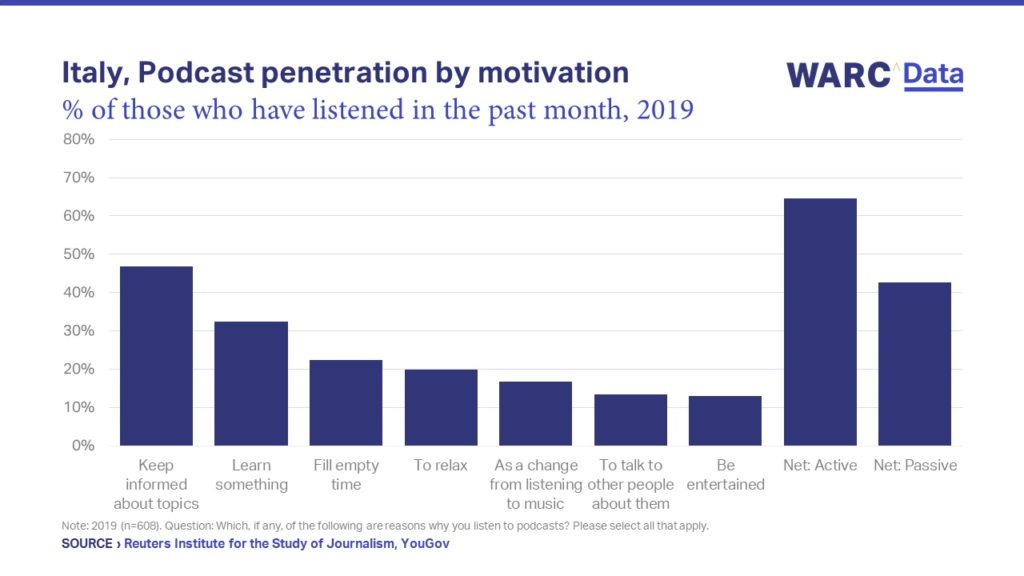
Looking at the image below (taken from the study carried out by Reuters Institute for the Study of Journalism and YouGov, quoted by brand-news.it) one can discover some of the reasons for the increase of podcasts in Italy according to the users themselves: in first place is the desire to keep up to date on various topics, followed by the possibility to learn something new, to fill some free time, to relax, to vary from listening to music, to be able to share what has been learned with other people and, finally, to obtain an entertainment system.
Why make a podcast
Even in light of what has been written, it should seem obvious that the decision to create a podcast can turn into one of the most effective strategies for content dissemination, education and entertainment, as well as fortifying our brand.
But what makes this medium so powerful? First of all, podcasting offers a unique way to interact with a specific audience: unlike many other content formats, podcasts allow you to literally get into listeners’ ears, establishing an intimate and personal connection. This level of engagement is difficult to achieve with traditional formats such as blogs or videos.
In terms of brand building, podcasts are a formidable ally. Whether it is a personal or corporate brand, this format allows for authentic storytelling, sharing experiences, and showcasing expertise in a given field. When people listen to a podcast, they spend valuable time on that content, which results in greater attention and a longer-lasting memory of the message conveyed. This engagement can turn simple listeners into true brand ambassadors.
From an educational perspective, podcasts offer a flexible and accessible platform for learning something new. Think of how many times you have listened to a podcast while driving, exercising, or just relaxing. This flexibility makes it easy to assimilate new information without having to devote exclusive time, a not inconsiderable advantage in our fast-paced world.
Entertainment is another key reason why people choose to create podcasts. The ability to tell stories in a compelling way, explore unfamiliar topics and conduct thought-provoking interviews attracts a wide audience seeking content ranging from unsolved mysteries to tales of everyday life. Here, authenticity plays a crucial role: successful podcasts often owe their appeal to the genuineness of their creators.
In addition to these motivations, podcasts also offer a springboard for community building. Listeners are not just passive; they can interact, share opinions, and become part of a larger conversation. This interactivity can be leveraged to better understand audience needs, receive feedback, and create increasingly targeted content.
Finally, we cannot overlook the content marketing aspect. Podcasts can become a key component in a well-orchestrated marketing strategy because they help to diversify communication channels and can be integrated with other content, increasing the time users spend on the site and thus boosting SEO metrics. In addition, podcasts can serve as a call-to-action format for advertising campaigns, offering additional monetization opportunities.
Who creates podcasts: reasons for podcasting
Podcasts are an effective way to disseminate valuable content, build a personal or corporate brand, and create a community of listeners; they can be used to educate, entertain, or inform on various topics, reaching a specific audience in a direct way. Making a podcast allows for a deep and personal connection with listeners, ensuring an intimate interaction that other content formats fail to achieve.
For these reasons, podcasts have proven well suited to support the motivations and goals of a wide range of people and organizations: from individual creators to large corporations, the podcasting landscape is extremely diverse. Individual creators often start their own podcasts out of passion on specific topics, sharing personal experiences, expertise or, simply, providing entertainment. This format allows them to build a loyal community and reach people with similar interests from around the world.
Companies and organizations use podcasts to expand their digital presence and strengthen brand awareness. Through corporate podcasts, they can offer themselves as experts in their field, share company news and updates, or tell stories that reinforce their brand message. In addition, traditional media such as newspapers and TV stations are also embracing podcasting as a way to reach a broader, younger audience by producing content that explores in depth topics covered briefly in other formats.
Podcasts and content marketing: the evolution of podcasting in digital marketing
Podcasts have therefore emerged as a key element in the field of content marketing, offering an authentic and intimate way to connect with audiences. This intimacy stems from the very nature of the format, as mentioned: listening to a podcast is an action that directly engages the listener, creating a bond that other content formats can hardly match. The voice of the presenter, the stories told, and the quality of the production all contribute to building a relationship of trust and loyalty between creator and listener.
One of the most powerful aspects of podcasts in content marketing is their ability to improve brand awareness. A well-curated podcast allows a brand to become known in a nonintrusive way, offering valuable content that attracts and holds the audience’s attention. This can be especially effective when the podcast targets a specific niche market, creating a community of listeners who feel directly connected to the brand through relevant and consistent content.
In addition, podcasts are an ideal vehicle for strengthening customer loyalty. Podcast listeners tend to be very loyal, subscribing to their favorite programs and looking forward to each new episode. This loyalty can be leveraged to build an ongoing relationship with customers, keeping them engaged and strengthening the brand bond over time.
In addition to improving brand awareness and loyalty, podcasts also offer the opportunity to generate qualified leads. Valuable content that solves specific problems or offers useful insights can attract a quality audience interested not only in the podcast content but also in the products or services offered by the brand. Podcasts can include strategic call-to-actions, such as invitations to visit the website, download exclusive materials or sign up for newsletters, creating a pipeline of potential customers.
Finally, podcasts offer added value to existing customers. They can provide updates on new products, insights on industry-relevant issues, interviews with experts, and testimonials from satisfied customers. This not only keeps current customers updated and informed, but also makes them feel valued and engaged, enhancing their overall experience with the brand.
Podcasts and SEO: opportunities and visibility
In recent years, podcasts have carved out a role not only as powerful communication and entertainment tools, but also as strategic components for improving a website’s SEO. The inclusion of podcasts in the context of a well-planned SEO strategy can have significantly positive effects, increasing a site’s visibility, authority, and engagement. Let’s see how.
One of the first and most obvious opportunities offered by podcasts concernsincreasing dwell time on the site. When users visit a page that hosts a podcast, they tend to stay longer to listen to the episode. This increase in dwell time is a positive signal to search engines such as Google, as it indicates that the content is relevant and engaging. The more time users spend on the site, the better rankings on search engine results pages can be, helping to improve the overall visibility of the site.
Another significant benefit is podcast transcripts and show notes. Transcribing podcast episodes and including the transcripts on the site provides relevant keyword-rich text content that search engines can index. This not only makes the podcast content accessible to those who prefer to read, but also allows the site to appear in search results for a wide range of queries related to the topics covered in the podcast. Show notes, which summarize the main points of the episode and often include links to external resources, further reading and references, further enrich the content of the site, providing added value to both users and search engines.
Another crucial aspect in which podcasts can positively influence SEO is link building. Podcasts tend to be shared and linked to by other websites, blogs, and social media platforms: when a podcast episode is mentioned or reviewed, or when other websites insert direct links to the episodes, this increases domain authority; in addition, podcasts can generate brand mentions on various platforms, further increasing online visibility.
It is important to note that optimizing podcasts for SEO is not only limited to the creation and distribution of quality episodes, but also includes the use of keyword-optimized titles, detailed descriptions, and appropriate metadata. Using tools such as SEOZoom, we can identify the most relevant keywords and keyword phrases that will have the greatest impact on the search queries of our target audience.
In addition, podcast hosting platforms often offer features that can help optimize content distribution and discovery. These platforms provide detailed statistics on audience numbers, listener demographics, and other crucial metrics that can drive further SEO optimizations.
Finally, cross-channel promotion of podcasts using social media, newsletters, and other content marketing strategies can further amplify the impact on SEO. Every mention and every share increases opportunities to get backlinks, improve domain authority, and attract qualified traffic to the site.
The spread of podcast advertising
The interesting news for those looking at this tool does not end there: on the promotion front, “podcast advertising” also seems to offer useful insights. Globally, this market segment was worth more than $479 million at the end of 2018, up 53 percent from the previous year, with even redder projections. In fact, forecasts from the IAB FY 2018 Podcast Ad Revenue Study speak of a jump to $1 billion in advertising investment through podcasts (both in the form of audio and within them) by 2021.
We are moving into an audio-first environment, as the IAB paper states, made up not only of podcasts but also of voice and on-demand content, which marketers definitely need to look at closely. And thus, podcast advertising may be one of the most dynamic channels in the near future, also distributed through connected objects that allow in-car enjoyment while traveling and especially voice assistants and smart speakers in the home as well.
The characteristics of podcast ads
Analyzing this tool even further, it turns out that podcasts can be a premium context for advertising, especially because of the ways in which they are enjoyed by users. In fact, in general, listening takes place while also carrying out other daily activities (we were talking about driving, but also household chores or outdoor sports), and this simultaneity may make ad skipping more unlikely.
Synthesizing and simplifying, it can be argued that “advertising on podcasts multiplies exposure rates, making statistics and vanity metrics happy, as well as the listener of course, because it has the virtue of being nonetheless unobtrusive,” as noted in an in-depth article on Inside Marketing. And it is no coincidence that baked-in ads-that is, ads created specifically to be hosted on the podcast and then integrated with content consistency as well-are also on the rise, currently accounting for roughly half of total podcast advertising.
By and large, the most widely used form of podcast advertising remains ads read by the program host himself (a derivation of classic radio advertising), followed by the equally traditional commercials read by an announcer, while recycled forms of advertising content broadcast on other channels (including those via radio) are rarer.
The duration factor is surprising: in more than half of the cases, ads placed in podcasts last between 60 and 90 seconds, taking advantage of the aforementioned favorable propensity of users toward this advertising. One in five marketers, however, prefer a short 30-second version so as not to overdo the invasiveness. The focus on the monetization system highlights the value of cost-per-thousand outweighing other forms of payment, but in 2018, the rise of fee-based systems is most notable.
IAB’s analysis of podcast advertising investment also allows us to find out what the goals of advertising investment are: the primary purpose of podcast advertising is to strengthen brand awareness and serves to support corporate campaigns, but in strong growth are reported ads related to content marketing and branded podcasts, often the result of partnerships and co-branding between entities from different sectors.
How to create a podcast
We have clarified what they are, what they are for, why, and who creates them: now let’s turn to the practical aspects and “how to make a podcast.”
Creating a podcast requires careful planning and a certain amount of effort: the process may seem complex, but by breaking it down into basic steps it becomes much more manageable.
The first crucial step is designing the content: we will need to determine what topic to cover, the tone to adopt and how to structure the different episodes. It is important to have a clear vision of your target audience in order to create content that meets their needs and interests. Planning the structure of individual episodes and the podcast as a whole can avoid improvisation and ensure narrative coherence.
Once the content is defined, move on to the recording stage. To achieve high-quality audio, it is essential to use a good microphone: investing in a dedicated microphone, rather than using the one built into the computer, will make a big difference in the clarity and professionalism of the sound. In addition to the microphone, we will need recording software to capture the audio, and programs such as Audacity or Adobe Audition are popular choices for their ease of use and advanced features.
After recording, the next process isediting, which involves cleaning up the audio, removing background noise, and adjusting the volume to ensure a pleasant listening experience. Editing software such as the aforementioned Audacity and Adobe Audition offer various tools to improve sound quality and add special effects if needed. While editing, you can also add jingles, intros, and outros, which make the podcast more professional and recognizable.
Once the episode has been recorded and edited, we proceed to publication. In order to make our podcast accessible to the public, we need to upload it to a podcast hosting platform, which act as a central hub from which our podcast will be distributed to various streaming platforms. Services such as Anchor, Libsyn or Buzzsprout offer different features, so it is helpful to choose the one that best suits our needs.
The last step is distribution. After uploading the episode to a hosting platform, we can make it available on various streaming services such as Apple Podcasts, Spotify, Google Podcasts, and many others. These platforms offer analytics tools to monitor the number of listens, where the audience is coming from, and other crucial data that can help us improve and optimize our podcast over time.
Podcast equipment: what you need for a professional product
To start recording a podcast, it is essential to have the right equipment. As mentioned, the microphone is probably the most important tool, and a good quality tool can make the difference between a professional and an amateur podcast.
Another essential item is a computer equipped with recording and editing software: programs such as Audacity (free and open source) and Adobe Audition (more advanced) offer a wide range of features for recording and editing episodes, provided you have good technical hardware to support these programs.
Headphones are equally important for monitoring audio while recording: if of high quality, they allow us to perceive sound details that might be missed while listening on standard speakers, allowing us to make corrections in real time.
We cannot forget the importance of a proper recording environment: even the best microphone can pick up unwanted ambient noise if it is not recorded in a quiet place. Soundproofing panels and anti-pop screens are useful to further improve audio quality.
Finally, other useful accessories may include microphone arms, anti-vibration stands, and audio interfaces. All of these tools, although not essential, can help make the recording process easier and improve the final quality of the podcast.
Where podcasts are published and how they are listened to
After completing the creative part, you need to think about the distribution of the product.
Podcasts can be published on a variety of platforms, each with its own unique features, but all aimed at making content easily accessible to listeners. Among the most popular are Apple Podcasts, which is one of the pioneering services in the world of podcasting, just as prominent is Spotify, which has significantly expanded its offerings to include a wide range of podcasts, made accessible alongside music playlists and personalized recommendations. Spotify has invested significantly in exclusivity, signing contracts with some of the most celebrated podcasters and thus creating a diverse ecosystem that attracts a wide audience.
Google had also jumped into this area, developing Google Podcasts, which initially gained high visibility due to its integration with the Android ecosystem and prominent position in SERP – as well as the ability offered to synchronize content across different devices and to send personalized recommendations and features that facilitate the discovery of new content based on the user’s interests, thanks to data collected from the search experience with the Google account. In April 2024, however, the company finally abandoned the project, pushing harder on YouTube Music, in which it has concentrated all these services.
But it doesn’t end there: other platforms such as Stitcher, TuneIn, iHeartRadio, and Castbox offer additional opportunities to publish and listen to your own audio products. Each of these platforms has its own dedicated user communities and unique features that make them attractive to different audience segments.
Users can listen to podcasts through specific apps available on smartphones, tablets and computers, making the process of enjoyment extremely convenient and flexible. Each platform has its own dedicated app that allows users to download or stream episodes, create personal playlists, and receive notifications when new episodes are released. In addition, many podcasts can also be accessed directly from the websites of the creators or podcast networks, allowing listeners to listen to episodes without the need to install additional apps.