Local SEO: what it is and how to do SEO for local businesses
It is called local SEO or Local Search SEO and it is the activity of optimizing one’s online presence for local searches and, in particular, for Google’s Local Search. Which is, in turn, a kind of search engine side-by-side with the main one, capable of offering precise and localized results based on the queries entered by users, who get references to physical places where they can complete the task they need, such as buying a product or service. Local SEO is a key to all those businesses that depend on a geographically close customer base and sell directly to the public: the way of doing business has changed now and the information needs of consumers have increased, so being visible in search engine results pages and optimizing brand presence in local search is key to generating sales and reaching new customers.
What is local SEO
Local SEO is a set of techniques and strategies aimed at improving a business’ visibility in local sear ches on search engines such as Google.
Unlike traditional SEO, which aims to improve the organic performance of a site’s pages globally (nationally or internationally), in this case the competition context is that of a well-circumscribed geographic area, which we might consider the definition of locality closest to our purposes.
Local SEO thus emphasizes geographically specific queries and precise location mentions, which may be explicit or implied (based on the location of the user’s device performing the search).
Local search queries often follow a totally different search intent than others, and because of this, we usually cannot take the typical national/global approach.
The goal of optimization work is to make an activity stand out in searches made by users who are in a particular area or who are looking for services in that location. This can include both on-page optimizations such as the use of local keywords and off-page elements such as citations in local directories.
Local SEO: definition and importance
Local SEO is crucial for improving rankings in geolocated searches.
Let’s imagine a tourist looking for a typical restaurant or a souvenir store: he will use specific keywords along with the name of the city or neighborhood he is in or even without, taking advantage of the geolocation of his device and the interpretative capacity of algorithms. If our business is active in that area and is optimized for these queries, it will be much more likely to appear in the first search results, thus increasing its visibility and the possibility of attracting new customers.
In recent years, especially as a result of the pandemic, the Web has transformed our daily habits for physical shopping as well, and it is no coincidence that searches with the key “neartome,” “nearby,” or “near me” have virtually doubled, as Google frequently points out.
Who needs local SEO: which activities should work on a local basis
In this scenario, local SEO, or the activity of site optimization to achieve higher visibility positions among local and geolocated results on Google, has also almost naturally spread.
Optimizing one’s online presence for local searches is no longer an option, but a necessity for businesses that want to stand out in the digital landscape.
Due to its characteristics, local SEO is especially crucial for businesses that offer services in direct contact with the public, such as hospitality businesses (restaurants, hotels, B&Bs…), commercial activities, professional offices, medical services, and so on, which therefore need to put in place solutions and interventions on the site to climb positions over competitors and appear more reliable in people’s eyes.
This work allows us to reach the users closest to us and our business, and therefore potentially more interested in clicking on the results and buying what we propose. And it is not only the click on the site that is the result to be achieved: in most cases, the goal is to bring the customer to the physical location to complete the action or conversion. According to Google, 50 percent of users who perform a local search from mobile devices actually visit the store within a day.
In concrete terms, virtually any business that operates locally can gain tremendous benefits from local SEO. From restaurants to retail stores, medical centers to lawyers, any profession that serves a local community will benefit from increased visibility in local searches. Even services such as plumbers, electricians and IT technicians can see a significant increase in calls and service requests.
A case in point might be a small coffee shop in an urban neighborhood. By implementing local SEO strategies, the coffee shop can appear among the first results when someone searches for “best coffee shop [near me].” In addition, if it has a carefully curated Google Business Profile tab, with eye-catching photos, updated menu, and glowing reviews, it will have an even better chance of attracting new customers who may not have known it existed, but are attracted by the ease with which they found it.
Why local SEO is essential
Local SEO therefore represents an incredible opportunity for local businesses that want to compete with large chains or simply want to stand out from their neighborhood competitors.
In a saturated market, being found by nearby customers can determine the success or failure of a business.When we optimize for local SEO, we make it easier for potential customers to find us and interact with our business, which not only increases the visibility of our business, but also its credibility.
One of the most immediate benefits of local SEO is as mentioned the increase in in-store visits, which is directly reflected in revenue. In addition, local SEO helps build a stronger bond with local customers, as they more easily find contact information, opening hours and reviews, which helps generate trust and loyalty.
From the site’s perspective, then, optimizing local SEO means increasing the chances of getting targeted organic traffic to our pages, and more importantly increasing leads and conversions, as we will attract a more relevant audience of users to the site (and potentially to the location) and already well into the funnel.
In addition, having a precise strategy allows even the smallest businesses to stand out, even outperforming large national companies with unlimited capital, which typically focus on more generic, broad keywords and rely on the power of branding and corporate branding to get traffic.
Important statistics and insights of local SEO and local searches
To understand at a glance the crucial value of local-based SEO, we can refer to a number of global numbers and statistics gathered from various online sources.
- 97% of users use the search engine to find a local business.
- More than two-thirds of Google searches have local intent.
- 3-Pack results get 44% of actual clicks on the Google results page.
- Searches from mobile devices for “near me” have more than tripled and still grew by 130% in 2022 alone.
- Mobile searches for “near me” or near to me, which contain a variant such as “can I buy” or “to buy,” have grown 500% in the past three years.
- Searches from mobile for “near me today/tonight” have grown by 900%.
- Searches for “shopping near me” have increased by 200% in the past three years.
- Searches for local places with “near me” have increased 150%, faster than comparable searches that do not include “near me.”
- Mobile searches for “Open” + “now” + “near me” increased by 200%.
Moreover:
- More than 50% of “near me” searches lead to a store visit.
- 28% of “near me” searches result in a purchase.
These data confirm that the “near me” queries are not only also an indicator of changing consumer habits in searching for local businesses, but above all reflect a strong purchase intent.
This is one of the most relevant aspects of local searches: when someone searches for something specific for today or tonight or nearby, it is clear that they have a strong desire to act immediately. This results in an impressive conversion rate: nearly one in four people make a purchase when they search for businesses “near me.” However, many local businesses do not adequately optimize their online presence to benefit from these high-intent searches. This is a strategic mistake, as local searches represent a unique opportunity to attract customers with a propensity to buy.
And the global spread of smartphones has revolutionized the way people find and interact with nearby businesses, with Google becoming the centerpiece of this transformation. The era of consulting the Yellow Pages to find a local business is long gone: today, search begins and ends with Google. The correlation between smartphone advances and “near me” queries is obvious: Users use their mobile devices to search for nearby businesses, and Google has perfected its ability to locate and provide relevant information about these businesses.
What is Google’s local search
And so let’s talk about Google, which we said is the starting and ending point of almost all (even) local search.
Google local search is a kind of search engine integrated into the main search engine that offers geographically relevant results, localized according to the location of the user launching the query.
Simplifying to the extreme, the results are determined by the interaction of three factors-classical relevance, distance, and prominence, as we will see in more detail-and appear both in the classic Search SERP and as points in Maps, so that users can easily go to the location of the business or place of interest near the location where they are.
In addition to the type of business/service, a basic local search query usually includes information such as city name, neighborhood, or address, but by enabling device location, it is sufficient for Google to interpret a transactional intent to provide local results as an answer.
At the heart of this system is the so-called “Local Pack results,” the specific feature that generates as a response a set of featured local activities-classically three, which is why the feature is also often called “Local 3-Pack” or simply “3-Pack.” This feature usually sits at the top of search results (or at least in a position of strong prominence and prominence), directly below a map with placeholders, and is often enhanced by star ratings and relevant local information.
Google’s Local Pack is where most “near me” search activity takes place and makes it easier for users and potential customers to take action: in particular, the Click to Call option is useful and appreciated, resulting in more direct contacts for local service businesses.
Algorithms and the evolution of local search
The development of local SEO is intertwined with theevolution of search engines. In the early years of the Web, searches were generic and global, and local searches in particular were rudimentary and significantly less sophisticated than today’s standards.
Local queries often included specific geographic qualifiers, such as cities, zip codes, or neighborhoods, to help search engines identify the most relevant results. A typical example might have been “pizzeria Milan 20100” or “plumber downtown Rome”-users had to explicitly enter this geographic information because search engines did not have the advanced algorithms that today automatically identify a user’s location.
Optimizing sites for these local queries reflected this technological simplicity: companies tended to create specific pages for each location in which they had a presence. For example, a restaurant chain site might have separate pages for each city or even each neighborhood, all with nearly identical content except for variations in the location name. This practice, known as doorway pages, was one of the most common overoptimization techniques. Each page would be saturated with local keywords, sometimes unnaturally and redundantly, in an attempt to manipulate search engine rankings. Local keyword phrases were inserted in every possible part of the page: titles, metadata, text bodies, image alt tags, and even in internal links.
This over-optimization of keywords not only led to low-quality content, but often created a frustrating user experience. The more primitive search engines of the time could be fooled by such tactics, rewarding sites that would be penalized for the same behavior today.
However, as the number of users and online businesses increased-and with the concomitant development of technology, which made search engine algorithms increasingly sophisticated-the need to provide more specific and locally relevant answers emerged, and these practices began to be identified as spam and led to penalties, prompting SEO practitioners to develop more authentic, user-oriented strategies for local searches.
A significant turning point in the evolution of local SEO was Google’s algorithm update known as Google Pigeon, released in July 2014. On the back of the growing popularity of mobile browsing, Google understood that a new need was emerging for users to find answers “closer” in a physical sense to their location to conclude their search journey.
And so, local search emerged as a smart search tool for people looking for information about nearby businesses or services, and as a powerful opportunity available especially to small businesses, which can attract new customers interested in their offerings.
The system with which this revolution started was precisely the Google Pigeon algorithm, which aimed to improve and refine the ranking of local organic results, provided based on the user’s location and the list available in the local directory.
Location and distance are key parts of this new search system, which favors businesses closer to the searcher’s physical location. Another relevant feature is the evolution of the so-called local pack, linked to Maps, which lists and groups major local businesses located on Google, shown precisely when a query has local intent.
Google Pigeon dramatically improved the way Google handles local searches. tying the local search algorithm more closely to traditional web ranking factors; it also gave greater weight to user proximity and consistency of business information, improving the accuracy of “near me” searches. As a result, local businesses that had optimized their data and online presences saw a significant improvement in their ranking in search results.
The age of smartphones has further revolutionized local SEO. Users, in fact, began to do “on-the-go” searches to find immediate answers to their daily needs, such as an open pharmacy nearby or a restaurant for lunch. Today, most local searches are conducted from mobile devices, making local optimization imperative. According to a Google report, 46 percent of total searches are for local information, a figure that underscores the growing importance of local SEO.
How to do local SEO
Today, optimizing a website for local SEO requires a number of specific techniques necessary to intercept the volume of “near to me” searches, as we were also told by local search expert Luca Bove, whom we asked for his opinion precisely on local SEO techniques for e-Commerce visibility.
First, we need to go beyond including conventional local keywords: although including local keywords in different parts of the site (such as titles, descriptions and page content) remains important, it is equally crucial to take a more robust and integrated approach. Many local searches involve specific intents such as “near me” or “nearby,” so it is essential that optimization reflects these implicit variables.
Understanding the intent behind “near me” queries is essential, as it varies by business type. Pizzerias, laundromats, or auto repair shops are likely to receive more “near me” searches in relation to the frequency with which someone intends to visit this specific type of business-for example, the search “Pizzerias” shows three pizzerias within 5 kilometers of the office, where the search is located.
A professional services-based business, such as a law firm or marketing agency, may not encounter the same volume of “near me” searches, and so optimizing for “near me” is not + as meaningful. This is why, when searching for a service-based business, the local package results expand to a wider radius, casting a net across the city.
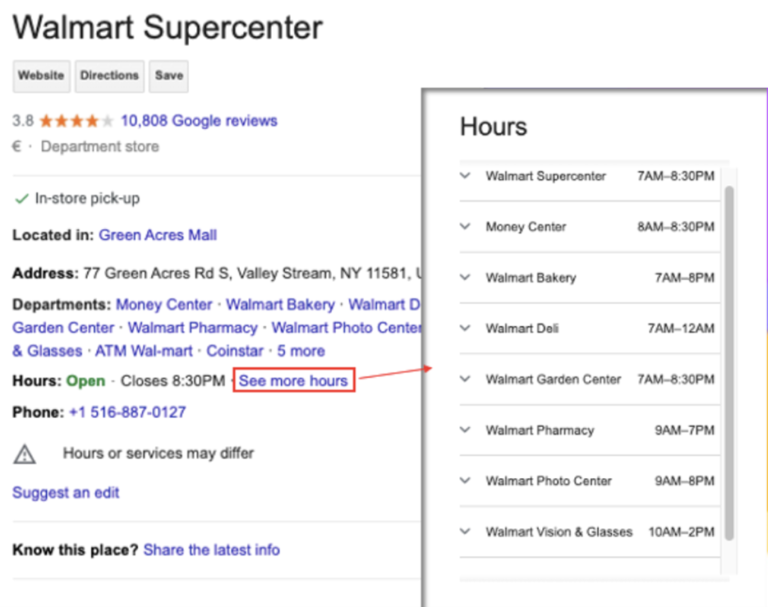
A crucial element of local SEO is the Google Business Profile. This tool, formerly known as Google My Business, allows you to create a detailed profile of your business that appears in maps and local search results. It is critical that the profile is completely filled out with all the correct information: opening hours, address, phone number, and photos of the business, making sure they are always up-to-date. Customer reviews are particularly influential: by encouraging positive reviews and responding promptly to negative ones, we will improve our reputation and signal to Google that the business is trustworthy and active in the community.
To further boost rankings in local searches, it is useful to use schema markup specific to local businesses. This helps search engines better understand business information, displaying it more accurately in search results. It is also important to obtain citations in authoritative local directories and build a strong network of backlinks from authoritative sites on a local basis as well, which strengthen online presence and reliability.
Still, creating relevant and geo-referenced content, such as blog posts that talk about our area of operation, mention local events, partnerships with other neighborhood businesses, or tell stories that relate to the community, can further enhance visibility. This content not only attracts search engines, but also local customers, solidifying your presence as an important resource in your geographic area.
Finally, if target audience analysis is a key step for any SEO strategy, for getting results in local search this becomes even more true: a site should never target an infinite and undefined audience, and even more so cannot do so if you are trying to stand out in a space that is “narrow” by definition.
This means that we must take advantage of every means to study and define our target audience, that is, the users to whom we should address our message using the words, tone and propositions that are most akin to them: thus we can identify in advance the potential customers to be attracted to the site and the store, develop offers that may prove most attractive to their needs, and adapt the language and tone of communication.
The tools for local optimization
The work on local SEO is therefore very specific, and in addition to the classic advice of optimizing the site in all its aspects – also providing content that emphasizes the value of the local offer, with “geographic” keywords, perhaps even trying to monitor the SERPs by setting Google search from other locations – you have to take great care of social management and, above all, the Profile tab of the business, which until recently was called Google My Business.
As we said in other insights, this free space provided by Google is one of the main tools for local SEO, so recognized also by digital marketers as well as by users, who find precisely these tabs in prominent positions on both Search and Maps when they perform localized searches.
Social media is also a relevant channel to connect with users and understand their needs in advance, because it creates a point of contact with the target audience and allows us to work on fortifying visibility and trustworthiness.
Another useful contribution in terms of visibility comes from listing the company on valuable local directory websites, such as Yellow Pages, Yelp and many others, or niche industry portals: this allows us to be more accurately recognized by Google for the scope we belong to, but also to be found more easily by users. The minimum information to be added is the so-called NAPW (acronym for Name – Address – Phone – Web, i.e. Business Name, Address, Phone Number and Website Home) and a detailed business summary.
No less important is then to improve our business site, through which we can offer a good user experience, even for those who use smartphones (now the majority of people who surf online): therefore, it is essential to have a mobile friendly site, ensure a good page loading speed, implement a simple navigation system between menus and categories, and then still show immediately the information necessary for users (contacts, address, opening hours and so on), properly use structured data to activate any rich results in Search and to refine Google’s understanding of the pages.
Ultimately, it means working by following the basic rules of SEO and “common sense,” and this also applies to practical aspects such as the inclusion of localized keywords in content (from title tag to meta description, from headings to images to on-page text and URL), always without exaggerating and forcing with inadvisable practices such as keyword stuffing – what matters is always to offer added value to the reader, we must never forget that!
This simple practice allows us to “localize” our Web site for the geographic area in which we operate (city, province, region etc.); for companies with multiple locations, it might become useful to create separate pages or Hubs of content for individual locations. Also, one should not be “static” but try to activate involvement with local community events and present articles and inherent information on the site.
How to use SEOZoom for local SEO
It is necessary to return to the clarification to be made with respect to the use of keywords: local search, as we have mentioned, includes two different types of queries. That is, both expressly localized ones-that is, those that contain a search string formed by a keyword plus the addition of a location (restaurants in Milan, dentists in Rome, and so on) -and implicit queries, which Google interprets as localized.
It suffices to do a test to understand this second aspect: simply typing “restaurant” on Google – via smartphone or desktop is indifferent – to obtain the same as localized results based on the geolocation perceived by Big G’s algorithm.
These are so-called “near tome” / nearby searches – again, the expression of proximity can be explicit or implicitly understood by Google – which create SERPs based very subjectively on the individual user’s location and history. For this reason, SEO tools cannot give objective answers for this type of keyword, but only general and so to speak “national” directions.
With SEOZoom we have various tools to keep an eye on interesting keywords and, as well as in classic strategy, study the moves of direct competitors.
Based on the premise just made, for expressly localized queries we have all the necessary strategic information at our disposal: search volume, level of competition, ranking possibilities, tools to optimize the search intent required by Google, and so on.
It is different for the other type of keywords, those near to me: in this case (and as far as explained), it is not possible to do a complete local analysis of a keyword or set of keywords with volumes and other data, but we can still use SEOZoom as a rank tracker and thus keep track of changes in ranking.
To do this, simply add the keywords to a project and select the SERP, keeping in mind that local volumes are not currently available.
How to work on local ranking
But what are the main aspects that drive local positioning? Google’s official page explains it, listing the three factors that, combined, help algorithms find the best match for the user’s search.
And thus, the three the criteria that drive the local search results algorithm:
- Relevance, which measures the degree to which the activity’s offerings match the search intent. Optimization for this aspect requires including complete and detailed information about the business, site, or Profile tab of the business to allow Google to better understand what we offer and match the profile to relevant search results.
- Distance, which precisely calculates the physical and geographic distance of each potential search result from the location used in a search. This applies both if the user specifies a location through a keyword entered in the query (e.g., when we search for “shoes in Rome”), and if Google automatically derives the location by calculating the distance based on the user’s known location data (location of their device via IP address or smartphone geolocation system).
- Evidence, which concerns the level of notoriety of a business. This factor is based both on a brand’s authority in the real world (as the guide explains, “famous museums, prestigious hotels, or well-known store brands that are known to many people are also likely to be prominent in local search results”), and on signals that Google gleans from the Web, such as links, articles, and directories. In addition, online reputation and the number and score of Google reviews also affect a business’s local ranking: the more positive reviews and ratings, the better the ranking. And then, because ranking in Web results is another determining factor, Google also urges the application of SEO best practices.
Through the combined use of these signals, Google’s algorithms-whose details remain strictly “confidential, so as to ensure that the ranking system is as fair as possible for everyone”-determine the placement of results. For example, they might determine that one business, although farther away from the user’s location, is more likely to offer him what he is looking for than another closer, and will therefore rank it higher in local search results.
How to measure the success of local marketing
And so, local marketers must adapt and evolve quickly to catch the “signals” and effectively measure the success of their strategies. The two authors point to 7 tactics and best practices for measuring the effects of local marketing campaigns that are valid even in times of crisis.
- Monitor Business Profile metrics
As also mentioned earlier, the former Google My Business is the most immediate and effective showcase for local SEO, and over the course of the pandemic the tool has taken on an even more central role, enabling businesses to stay in touch with interested potential customers and to communicate updates to them on the actual opportunities to take advantage of the service offered in light of the various regulatory provisions in place at the time.
Classically, among GMB’s most closely monitored metrics to measure the success of the strategy were map views and directions, but the new environment has made it important to be able to monitor (and on a monthly, rather than annual, basis) other statistics, such as Impressions/Displays from Search, Clicks on Site, and Clicks on Phone Calls, that can give us a picture of actual user interaction with the business card.
Indeed, with lockdowns and various restriction measures, consumers have moved beyond traditional search and adopted e-commerce options.Regardless of the product or service offered, every industry has been affected to some degree, and all businesses have had to come to terms with a new kind of need, “keeping customers informed while helping them feel safe.”
Therefore, all the updates to business operations-from temporary closures and schedule changes to outdoor or indoor seating availability-required quick and effective dissemination of information to consumers, and “Google Posts became a key tool for sharing news quickly,” especially after the introduction of the “Post COVID-19 option, which allowed businesses to share critical health and safety information directly in SERPs.”
- Measure all types of devices
The world now surfs from mobile, and the pandemic has only given a further boost to this dominance. Yet, experts explain, it would be wrong to fixate only on mobile benchmarks, which cannot be the only area of focus.
In fact, brands should likewise focus on analyzing desktop traffic, even on a monthly basis, “to identify immediate trends that can help uncover the current needs and expectations of site customers.”
- Using referral traffic to measure customer engagement
Refferal traffic to sites is not always a primary KPI, but “a secondary or supporting KPI depending on the story being told about customer engagement.”
With changes in the way Apple Maps, Yelp, and other local sources have provided opportunities for brands to share COVID-19 details about physical activities, “the measurement of referral traffic and increases from these platforms show how people check additional sources to continually verify information,” as well as reiterating the need for accurate information across the local ecosystem.
- Focusing on the performance of the holistic search strategy
Now more than ever, one should work with a “holistic,” or integrated and unified, search strategy, not dividing the efforts of organic campaigns from their paid counterparts.
In fact, today Google has “forced brands to own valuable search terms through ever-changing SERP layouts and integrations such as hotel ad feeds,” and so “adding budget for Local Search Ads or integrating Local Inventory Ads into listings can help customers find what they are looking for more efficiently.”
The advice, then, is to measure paid performance and, if they show they are a worthwhile effort to undertake, add them to the overall search strategy: the underlying goal is to reach and be reached by the customer, through whatever mode or channel.
- Monitor customer sentiment through reviews
Being able to monitor and know how to respond to reviews during a crisis has become an even more important element of local strategy and success: in today’s new environment, user feedback is critical not only in building brand image, but also in actually understanding how to address customer needs.
This is why some platforms, such as Yelp, openly relied on customers during the pandemic to get feedback on how activities are following health and safety protocols.
In general, understanding the senti ment around a business or brand, monitoring customer satisfaction, fluctuations in average star rating, and addressing customer concerns are all metrics that can help create positive sentiment, as well as “how quickly and how often the teams in charge respond to reviews and feedback have become metrics of success.”
- Leveraging Google Analytics to measure e-Commerce performance
Those in the retail industry who had not implemented the e-Commerce channel before are now forced to develop and execute it flawlessly. Commerce is moving almost exclusively online, and delaying further means lost business opportunities.
Day-to-day problems are there, between shipping time delays and logistical nightmares, so “it is critical for companies to ensure a seamless order process, with fast delivery times, to build a positive brand association.” Moving forward, however, toward normalcy, experts ask, how “will it be possible to really understand how physical stores are performing relative to digital shelves?”
In support comes Google Analytics, which offers a feature (now in beta) on in-store visits that can help brands visualize their omnichannel performance.
- Staying up-to-date on the most searched keywords
The target keywords of the business also need a pivot: in the past year, searches for [near to me], [curbside pickup] and [drive-thru] have grown at unpredictable rates, and new trends such as [contactless delivery] have emerged.
So we need to check whether we are actually monitoring trending keywords relevant to our industry, because-if not-we may miss opportunities to convert high-intent consumers.
Checking key terms from Business Profile insights can help companies understand which keywords should be optimized to continue reaching current and new customers, but refining the local marketing strategy also includes “reshaping the KPIs and metrics most important to the business.”
Reacting to the crisis to prepare for recovery
The unexpected COVID-19 pandemic has uncovered “new areas of opportunity for businesses, including new social distancing services, and skyrocketed both mobile and desktop purchases.”
As a result, Nyman and Abramson conclude, metrics that were once crucial to monitor to determine local brand marketing success have now become obsolete, and it is “critical to stay informed and up-to-date to recover from a largely tumultuous event and set your business up for a recovery and future that may be favorable.”
The tips and techniques for standing out in local SEO and dominating SERPs and Map Packs
In the wake of what has been written, it seems clear that it is crucial for businesses to have optimized local listings and an effective local marketing strategy that knows how to measure the success of the work: restaurants, retail stores, and other types of local businesses have many potential customers searching for their products and services, and Google’s SERPs are constantly evolving to show these results to interested users.
Examples of this are the continuous integrations of informational features in the local panel of Google search results, which allow the user to view useful and increasingly specific data with respect to the relevant business.
Going practical, Winston Burton ‘s article in Search Engine Journal presents us with 12 local search tactics that can be used to help a business improve its visibility in local SERPs.
- Managing information consistently
The first point is to manage all listings consistently and accurately, verifying the correctness of the NAPs (name, address and phone number, not forgetting the URL of the site’s home) in the various places where they appear, i.e., search engines and local directories, trying where possible to remove duplicate listings.
A local search platform among the many on the market can be used to simplify this work.
- Using structured data
Structured data is important to help Google better understand content and can help increase clicks, impressions , and conversions, and this also applies to local search.
Therefore, it is absolutely important to “implement structured data types such as local business, geocoordinates, postal address and reviews (which allow you to report local business, geocoordinates, postal address and reviews) to improve performance.”
- Taking advantage of the Business Profile tab
“If you are not using and optimizing your business profile on Google you are missing an incredible opportunity to make your products and services visible where it matters most,” the author points out.
To optimize the card, one must first include “as much information as is possible to include, as well as photos, menu items, descriptions, and service lines,” which is one of the most important aspects of local search optimization, spending time filling in all the relevant information, such as the menu, product descriptions, and so on, frequently monitoring the card to make sure that the information is always up to date.
This is even more true during times of “imposed” restrictions and hours, because providing incorrect information can generate a bad user experience-for example, if they find a store closed when the card indicated it was open, the customer may decide to go elsewhere in the future as well.
Today, it is crucial for businesses to update local search results to clearly communicate to potential customers that they are temporarily closed or that they offer special services, such as takeaway options for restaurants, even as Google has begun to show attributes of the store’s operational status within Maps.
Large retailers with multiple in-store departments can use the Activity Profile to include secondary hours; this function can serve to update as appropriate:
- Departmental hours.
- Senior hours.
- Drive-thru schedules.
- Delivery schedules.
- Takeaway hours.
- Visiting hours.
- Pick-up hours.
One should also not forget to update the Q&A within the company profile with relevant or timely details, such as:
- Closures or schedule changes.
- Canceled events and ticket refunds/changes.
- Volume of calls/emails and expected delays.
- Changes in procedures for appointments.
- Measures implemented to increase level of health and safety.
- Changes to services offered.
Still speaking about Google, e-Commerce brands should take advantage of Google features designed specifically to improve data communication with the search engine, such as the Google Merchant feed or Pointy, which allow them to intercept a large number of potential consumers “who search for your products and services every day, allowing them to see in-store inventory in a non-paying product tab across Google properties, including Images, Shopping and Maps.”
- Updating the status of events
It is also important to keep up with schema.org updates, which often introduce new structured data that is also useful for e-Commerce, such as those for reporting the status of events: using this tool is very important to allow users to know the current status of the event they are interested in.
Attributes of the EventStatus type include:
- EventCancelled, to indicate that the event has been cancelled.
- EventMovedOnline, to indicate that the event has been moved to online streaming mode.
- EventPostponed, when the event has been postponed and the new dates are yet to be determined (TBA).
- EventRescheduled, when the event has been rescheduled to a new date.
- EventScheduled, when finally the event is still scheduled as planned, with no changes.
Event information can be entered into the company profile via the events schema on the website or on external sources such as Facebook events, Eventbrite, and Meetup.
- Checking lists
Burton reiterates that it is crucial to always monitor the search results matched to the brand, particularly to identify:
- Automatic updates to operating status (“Temporarily closed” and others).
- Pending or suggested changes to operating schedules.
- Pending or suggested changes to attributes.
- Pending or suggested changes to activity details.
- Any other indicators of pending or suggested updates.
- Deactivated listings.
- Managing reputation
Online reputation management is key to ranking high in the Local Map Pack, and so one must work to attract positive reviews and provide a good customer experience; in particular, one must avoid leaving user questions or feedback unanswered, as this is a really negative signal.
People, in fact, trust reviews, and negative reviews are worse when the owner does not take the time to respond; if, on the other hand, he can provide an explanation, this action “potentially increases the trust of other users and could also help generate more business.”
Therefore, the advice is to always check and respond to reviews, both positive and negative, and focus on getting unsolicited natural reviews, while also leveraging the website to upload first-party reviews.
- Using hyper-local content
The goal of SEO is to provide a positive content experience across all devices and platforms to help end users meet their information needs.
In local SEO, this can mean trying to publish quality and unique content tailored to individual locations related to the business-this hyper-local content can help improve visibility among potential customers located nearby.
Also useful is the use of hyper-local terms in the on-page optimization strategy, i.e., optimizing headings, titles, metadata, alt-text, and text, as well as continuing to provide information about the prevention and safety protection systems implemented: all of this can create “trust from the end user’s point of view and will also help to get great reviews,” because “demonstrating that you are taking the right precautions can actually help sell more products and services when customers come to pick up food or store at the store.”
- Using continuous messaging systems to connect with customers
Using an always-on messaging system to keep in constant contact with customers is one way to increase their trust and respond to their needs in real time.
One practical way to achieve this is to download the Google app and activate integrated messaging, which will allow customers to reach out to your business.In cases where phone calls are unavailable or at times outside business hours, messaging can help customers still get the assistance they need.
- Monitoring trends
Closely monitoring Google Trends can help you understand changes in search interest and behavior related to keywords and topics relevant to your brand and industry. The next step is to analyze the keywords most valuable to your business and observe how searches for those items are performing, and then again monitor site performance so you understand what user conversions are during this period and update your forecasts and reports in light of these insights.
- Optimizing for voice search and mobile devices
“We live in a world where users are constantly asking questions, and your brand should provide the answer even when consumers are asking a digital assistant,” says the author, who reminds how the site should also “be well optimized to provide answers to common questions about products and/or services.”
To optimize content for voice search and suggestions on what to include, you can first look at internal search metrics and analytics to see what common questions people are asking about the business, possibly using third-party tools and Google’s People Also Ask (PAA) feature.
And “since the majority of local queries occur on mobile devices,” it is important that the site is optimized for mobile devices with high-quality images, content and fast load times.
- Tracking rankings and building local landing pages
“Rankings aren’t everything, but they can help you track the success of your local search campaign at the location and zip code level,” stresses Burton, who recommends “creating local landing pages that provide a good user and page experience, including responsiveness, fast load times, the latest schema code base, call-to-actions and design elements.”
All of this can help the brand position itself in all locations and improve conversions.
- Links are always important
The last tip refers to one of the “cornerstones” of SEO, which is getting high-quality links from sites, blogs, local and general newspapers, because these links “from reliable sources with good content can help users solve problems and build trust and credibility” toward one’s site.
Links are still a very important factor that can improve site and brand visibility and help strengthen local search presence, something that is more important than ever given today’s competitive SERPs.
Being visible to win over consumers
Consumers are looking for brand-related products and services, so being visible is the only way to intercept their needs and win new customers.
With Winston Burton’s 12 tips, you can optimize your work to reach the top of SERPs even for local search and dominate local results.